Satellites are objects that orbit the planet in a certain period of revolution and rotation. These celestial bodies also have a track point in surround a planet. That is what is known as an orbit. The satellite can orbit Earth because gravity will retain the position of objects in place. You need to know anyway, in orbit, there is a term apogee (farthest point from Earth) and a perigee (nearest point from Earth).
There are two types of satellites, namely natural and artificial satellites. Natural satellite is a celestial body orbiting naturally in a planet. Consciously or not, I'm sure you've seen the satellite directly. Yes, the name of the Earth's natural satellite is owned by the Moon.
In addition, there are five natural satellite of the largest ever found a human, that Ganymede (Jupiter), Titan (Saturn), Callisto (Jupiter), Io (Jupiter) and Moon (Earth). Artificial satellite can be defined as celestial objects created by human hands based on the functions and needs. To be sure, the artificial satellites you can not see with the naked eye, as when looking at the moon.
there sat inner satellites and other many more man-made satellites are designed so that for a specific purpose, such as telecommunications, research, and observation of outer space objects.
Satellite foundation flashback
The first satellite was Sputnik 1 launched men.
After knowing the natural satellite and artificial satellites, the next question is what is the first satellite created humans? The first satellite launched Sputnik 1 satellite is the man that made the Soviet Union in October 1957 and designed directly by Sergei Korolev and Kerim Kerimov who acted as his assistant.
The function of the Sputnik 1 is not to identify the density of the upper atmosphere. Furthermore, by conducting experiments to bring people living thing into orbit, in November 1957, the satellite Sputnik 2 was launched.In May 1946, through experimental research space vehicle to orbit the world, Rand Project Air Force issued with preliminary design of the satellite. The satellite design intended for the development of science.
In June 1961, the American Air Force, using various facilities of Mata Space Network of America (The United States Space Surveillance Network), cataloged at 115 satellites orbiting the Earth.
Types
Scientists create a satellite with a variety of uses. Here are some examples of artificial satellites and their role.
1. Satellite astronomyThe telescope-shaped satellites floating in space and is used for observation of distant planets, galaxies, and other outer space objects.
2. Satellite communicationsOne of these artificial satellites in orbit often using geostationary or geosynchronous orbit. These satellites are also commonly installed in space for telecommunications purposes. Installation is frequently used radio to microwave frequencies.3. Earth observation satellitesAs the name implies, these satellites are deliberately designed to observe the Earth, not intended for military purposes. The parts were observed synthetically this satellite is meteorology, environment, map making, and so on.
4. Satellite navigationThese satellites are used to measure the distance between the buildings and other buildings. The measurement typically uses radio signals that are connected with the receiver on the ground. This was done to determine the location point. One type of satellite navigation is often known GPS satellites belonging to the United States and Russia's satellite Glonas.
5. spy satellitesOne type of these satellites are used for military purposes, namely to spy on the presence and movement of the opponent.
6. Satellite weatherOne type of satellite is often primarily used in the interests of climate on Earth observation as well as the weather.
7. Satellite miniatureWhen viewed from the weight, type of satellite is small and lightweight, the mini satellites (500-200 kg), micro-satellite (under 200 kg), and nano satellites (under 10 kg).
Evidence
- Satellites first orbiter launched on August 17, 1958 to orbit the moon but did not succeed named Pioneer 0.- The first artificial satellite orbiter Soviet Union, which successfully orbited the Moon Luna named 10.- The first successful orbiter satellites orbiting the planet Mars was named Mariner 9.- The first satellite was named Explorer 1, United States.
VSAT - IPVSAT terminal is transmitting and receiving satellite transmissions are spread across many locations and connected via satellite using a satellite dish. VSAT is an important transfer media for data communication. Although not a perfect solution for LAN / WAN, VSAT satellite technology offers several advantages not possessed by terrestrial networks. In terms of range, a GEO satellite (Geostasionary Earth Orbit) can cover more than a third of the earth's surface. Such a broad coverage area is economically cause satellite system is much cheaper than if it had to build a fiber optic network or other terrestrial networks for coverage of the same. VSAT satellite communications network for voice and data transmission ensures the reliability (reliability) the success of the relationship of the foundation 99%. Besides, surplus no less important is the ease and speed of installation of VSAT terminals. Unavoidable losses of these systems is the time delay (time delay) is quite large, the noise and the echo (echo). On the other hand, there are several advantages, including satellite communication is very effective to reach areas unreachable by other communication tools. Satellite communications can replace with good functions of the submarine cable. Before there is a satellite communication system, communications between continents is done by using a submarine cable. Satellite communication systems are also advantageous in the operation of domestic long-distance telephone, and television networks, but it also has the ability to handle data facility of interconnecting computer terminals anywhere and satellite communication systems have multiple access capability.
SCPCtechnology SCPC (Single Channel per Carrier). SCPC VSAT technology is the use of high-quality dedicated bandwidth because it uses its own channels that provide maximum service quality assurance for data communications, voice, Point-of-Sales (PoS) or video conference as a point-to-point.SCPC suitable for companies that need to communicate with a wide bandwidth and high performance such as agribusiness, mining and others. Commonly used in enterprises with a high intensity level of communication, both data and voice on an ongoing basis, such as oil and mining companies.
X . I
Miscellaneous Satellites
Satellite is an object that orbits another object with a certain period of revolution and rotation. In nature there are two satellites that we know that natural and artificial satellites satellites, examples of natural satellites adalh months as a satellite of the earth. As for the artificial satellites are legion and we shall see hereafter.
TYPES OF SATELLITE MADE
artificial satellite is a satellite that is deliberately created by humans for specific purposes, such as for the transmission of information or to monitor what is happening on Earth. and below is some kind of artificial satellites:
1. Astronomical satellites are satellites used for observation of distant planets, galaxies, and other outer space objects. example: hubble satellite that was launched in 1990 that is used to photograph rose nebula

2. Communications satellites are artificial satellites are placed in space with the goal of telecommunications using radio at microwave frequencies. Most communications satellites use geosynchronous orbit or geostationary orbits, although some of the latest type using low Earth orbiting satellites. Example: Satellite television and the first information, the satellite Telstar 1 in 1964

3. Earth observation satellites are satellites specifically designed to observe the Earth from orbit, but intended for non-military uses such as environmental monitoring, meteorology, map making, etc. example: LANDSAT satellites used to observe the Earth's surface

4. Navigation satellites are satellites which use radio time signals transmitted to the receiver on the ground to determine their exact location on the surface of the earth. One of the satellite navigation which is very popular is the GPS of the United States but it is also the Russian Glonass. When the view between the satellite and the receiver on the ground there is no interference, then by means of a satellite signal receiver (GPS receiver), can be obtained position data in a place with few meter accuracy in real-time.

5. Spy satellites are Earth observation satellite or communications satellite used for military purposes or spying. example: defense supporting satellite (DSP) is used to give an early warning in the missile launch. DSP has been in use since the Gulf War in 1991 America

6. Solar power satellites are proposed satellites made in high Earth orbit that use microwave power transmission to beam solar power to very large antenna on Earth that can be used to replace conventional energy sources. example: Ikaros satellite made in Japan.

7. Space stations are man-made structures that are designed for human habitation in space. A space station is distinguished from the others by the absence of air space shuttle main propulsion or landing facilities; And other vehicles are used as transport to and from the station. Space stations are designed for medium-term living in orbit, for periods of weeks, months, or even years. The space station is also used to study the long-term effects of space flight on the human body and provides a platform for more and longer to research scientific of which has been provided from other space vehicles. example: the international space station orbiting the Earth at an altitude of 360 km, and began to operate on 2 November 2000.

8. Weather satellites are satellites used to observe the Earth's weather and climate. For example: The first weather satellite flown by NASA, TIROS 1 flown in 1960.

9. Miniature satellite is a satellite that is lighter and smaller. The new classification was made to categorize these satellites: mini satellites (500-200 kg), micro-satellite (under 200 kg), nano satellites (under 10 kg). example: five satellites were launched from the International Space Station on Thursday, October 4, 2012 that called Cube Sat which is used for a variety of missions such as earth observation, photography, and technology demonstration with the sending LED pulse or Morse code to test optical communication systems .

X . II
Utilization of satellite technology
Many interested parties to utilize the satellites for reasons of efficiency. Satellites can send signals to many earth stations at once, with no fee increases, although the farther distance . power satellite range is not limited, although each satellite has different coverage areas, referred to as foot point. In other words, there are areas where from a satellite can be received very well, and there are areas where the satellite signal was captured less than optimal, and some areas that were not able to capture the satellite signal.
The satellites are placed in a geostationary orbit (GEO), with an altitude of 35,000 km, is generally used for the needs of the television broadcast. Besides, who placed closer to the earth, the satellites Low Earth Orbit (LEO), and then with an altitude of 400 km - tens of thousand km, as well as satellite Mid-Earth Orbit, which have got an altitude of about 15,000 from the face of the earth, both used for needs services personal communications, such as cellular phones.
In general, the satellite can be divided into two types, namely natural and artificial satellites satellite. Natural satellites have diverse sizes and around primary celestial bodies. for example c: The moon is a satellite of the earth, and the earth is a satellite of the sun. Man-made satellite launched into orbit around a celestial body such as the earth or the moon.
Usefulness of artificial satellites are to:
a. Communication between places on the earth's surface
b. Being a reference point to establish a location in space
c. Observing the Earth and its environment
d. Collect and report scientific information.
Satellite communications can receive, amplify and emit a sound signal,
music, TV, telephone, telegraph and data from one point to another on the earth.
The utilization of satellites for educational field, according Polcyn (1973), satellite communication has caused tremendous possibilities for the dissemination and enrichment of the human learning. Where millions of TV viewers across several continents have witnessed historical events great in remote places, and even in the month.
Utilization of satellite communications to health care for example is Alaska Medical Project (The Alaskan Medical Project) which took place in 1971 and 1974 to 1975 (with ATS-6) is the utilization of satellites for public health services in rural Eskimos are generally remote, difficult to be contacted, and lies in areas that are naturally prone. This communication system other than for the purposes of relations emergency care, diagnostic, and giving advice, is also used for social communication among patients who were evacuated to a hospital far from his family.
Alaska Education Project was inaugurated called The Action Study of Educational Use of Satellite Telecommunications in Remote Communities Alaskan operations began in October 1971. The purpose of this project is to investigate the possibility of a wide range of broadcast services that are geared specifically to the heads of schools and rural communities. The most important objective of this project is to enable teachers through experience can develop a plan the optimum utilization of existing satellite telecommunications. PEACESAT project was organized in 1971 by using the master terminal in Hilo and Honolulu, Hawaii. Both the master station be attached with 16 earth stations capable of sending and receiving in 16 countries in the Pacific region.
While the University of the South Pacific project carried out in 1974 by using ATS 1 and ATS-6 to serve 11 countries in the South Pacific. In brief, the project aims to expand the role of universities in delivering lectures for students of pre - diploma level in their own neighborhood.
In the Rocky Mountain region of the United States in 1975 implemented projects tahun1974 and Technology Demonstration Satellite (Satellite Technology Demonstration) for the delivery of education and health services for rural communities. This project makes use of live television from the satellite to improve the quality of education in small schools located in isolated places in the region.
In general, the project aims to stimulate rural development through the integrated telecom systems. These projects were specifically intended to improve the quality of elementary teachers, teach useful skills to students, demonstrating the potential value that belongs to the satellite for the development of mass communication.
In 1971, the International Telecommunication Union (I T U) satellite classifies into three parts, namely:
1. mobile satellite
Mobile signal is that service ships and aircraft (for the purposes of maritime navigation, and cars).
2. fixed satellite
For long-distance communication services (regional, domestic and international).
3. satellite broadcasting
For distribution of television channels and radio, broadcasting directed to a roof antenna intended to acceptance of the individual or community.

Then how artificial satellites during this time can stay on top around the earth without falling? The answer is because of several factors ranging from the height, style, until the components of the satellite itself.
The force of gravity is able to draw objects such as artificial satellites falling to earth. But scientists can make the satellite can survive above by balancing the gravitational pull and style centrifugal. As well as the speed of the satellite orbit very quickly.
At first, the rocket must fly at an altitude of 100 to 200 kilometers above the Earth to get into space. Once in orbit predetermined altitude, the rocket began to go to the side with a speed of up to 18,000 miles per hour. According to Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts.

In order for artificial satellites can stay in his lane, the satellite must have styles like those of the moon. The difference is an attractive force of gravity is greater than the artificial satellites interesting month, because the location of the satellites closer to Earth than to the moon.
To obtain a balance between the force of gravity and force away the artificial satellite must move faster than the moon. If the satellite is moving too slow, then the satellite will fall back to earth. Conversely, if it is too fast, then the satellite will be detached from the force of gravity.
As explained in the video above, the balance between the two styles that can be achieved if the speed of the satellite is about 27,000 km / h as on international satellite ISS, or the GPS satellite has a speed of about 16,000 km / h with the two distance difference. At that speed, the satellite will continue to circulate around the earth. According to the following equation:
Satellite = GM / R, with:
V = velocity of the satellite around the Earth
g = the gravitational field of the earth worth of g = GMM / R * 2
M = mass of the earth
R = radius of the earth
If the style is equal to the force of attraction centrifugal F12 = F G S, the satellite can survive the sky without falling to the ground due to the pull of the earth is much stronger. In accordance with the following equation:
F12 = k m1.m2 / (R + h) * 2, wherein:
F12 = gravitational pull between the Earth and the satellite
k = constant Gauss (0.01720209895)
m1 = mass of the earth
m2 = mass of the satellite
R = radius of the earth
h = height of the satellite above the Earth's surface
So that the satellite can rotate continuously in orbit without falling into the earth, then there should be one other force acting on the satellite, so there is a balance between attractive force F12 is referred to as a centrifugal force that magnitude are:
FGS = m2.v2 / (R + h)
FGS = Style centrifugal (style that leads off the track)
m2 = mass of the satellite
v2 = speed satellite
R = radius of the earth
h = height of the satellite from Earth surface
One reason for his fall artificial satellites, because the fuel is exhausted and component is not good so within a few weeks into space garbage or fell to the earth. Or because the elevation is achieved when the slide is not appropriate, according to McDowell is around an altitude of 2000 km from the earth's surface. This makes the friction of Earth's atmosphere satellite circuitry can affect the balance of the satellite.
What about the height of the satellite should be able to survive long in the sky? Precise orbit altitude often called are in an area called the Geostationary Orbit.

Geostationary orbit is a geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator (0 ° latitude), with orbital eccentricity of zero. Of the Earth's surface, the objects that are in geostationary orbit will appear stationary (not moving) in the air for a period of such objects orbit around the Earth is equal to the rotation period of the Earth. Orbit is very attractive to operators of artificial satellites (including satellite communications and television). Because the location is constant at 0 ° latitude, satellite locations only distinguished by its location in longitude Earth.
Geostationary orbit is very useful because it can cause a satellite as it were silent on one point on the surface of the Earth is rotating. As a result, an antenna can point in one particular direction and remain in contact with the satellite. Satellites orbit the direction of the rotation of the Earth at an altitude of approximately 35 786 km (22,240 statute miles) above ground level.
In addition to Geostationary Orbit earlier there are still two other orbit at an altitude of 200- 1200 km, which is called the Low Orbit or LEO (Low Earth Orbit) and M E O (middle earth orbit) LEO and M E O layout is much lower than the location of the Geostationary Orbit, in orbit LEO satellites rotate faster than the rotation of the earth, that's orbiting satellites LEO can not work with one satellite only, as an example of the GPS satellite has 20 satellites to be able to work, the GPS satellite is rotating around the earth 8 times 1 day, meaning that the satellite will rise and set in 4 hours, that's why so many in need satellites to work .
Satellite long life of about 10 to 20 years. At that time also launched new, more powerful satellites to replace old satellites are dead so space garbage.

X . III
The location and direction of the satellite launch
Generally a space port must have an area large enough so that if a rocket exploded he will not endanger human lives around the launch site.
Generally a space port must have an area large enough so that if a rocket exploded he will not endanger human lives around the launch site.
The preferred location is usually located near the equator to the east in order to take advantage of the speed of rotation of the Earth (465 m / s) maximum, and is a good orientation towards a geostationary orbit. Moreover, this increases the mass ratio of orbit. For polar orbits, these aspects do not apply. For safety, a launch path over water or bare ground is important.
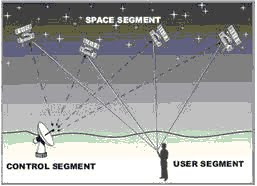
Satellite Transmission Network

Satellite is a tool in the orbit of the earth specifically to accept or deliver data wire memory flyer (without cables). communicate via radio frequency. Satellite communications are similar to line-of-sight microwave (transmission in a straight line / L o S), only one of the station, a satellite, orbiting above the Earth. Satellite acts like an antenna and repeater very high. As a repeater, serves to receive a wave microwave signal from the earth station, translated frequency , then amplified to be transmitted back to the earth in accordance with that coverage which is the location of the destination or the receiving earth station. In communications GEO (a satellite communications system that at most) position of the satellite is about 36,000 km above the earth. Satellite communications is a Relay Station or Repeater wave microwave placed in space. These satellites receive radio signals at a certain frequency field of the earth after amplified and converted to fields of different frequencies.
The satellite is a relay station. Satellite receives on one frequency, amplify or repeat signals and transmitting at other frequencies. Requires geo - stationary orbit, high 35.784 km (William Stallings, Data and Computer Communications 7th Edition).transmission of data
Media data transmission by using satellite is an interconnection of data communication using satellites placed outside the earth with a certain height where the carrier signal using a frequency specific emitted from the station earth and reflected by the satellite to be directed to the earth's surface more as long as the coverage the satellite area.
For the implementation of the communication, or a satellite must orbit around the earth rotating. Orbit is used orbit Geosynchronous where using this orbit a satellite can reach a third of the earth to a height of 36,000 Km (22,300 Miles) from the surface of the Earth, the satellite reached this height has a trajectory around the earth for 24 hours so it will always appear stationary to a point on the earth's surface.
This orbit satellites using an extremely rewarding to control the cost of the satellite is relatively lower and the relationship was never broken.
X . IIII
How satellites work
The workings of a conventional satellite system

By sending a signal from the computer and relayed by satellite without having done processing in the satellite. The weakness of this method, the computer that is connected directly to the satellite had to work for 24 hours. If one computer is turned off, the connection to the computer is dropped. The advantage of conventional communication satellites can be used without the need to be modified. Computer in satellite serves to store temporarily in-formation that can automatically do.
The workings of the transmission of data via satelliteUtilization of satellite communications system has provided the ability for humans to communicate and obtain information from various parts of the world simultaneously regardless of their relative distance. The basic components of a satellite transmission are:
Earth stations, used to send and receive data
Satellite, also called transponders
PCs using the Internet by satellite networks are categorized like wireless network by using microwaves. Microwaves will be transmitted and processed by a satellite earth station which is then transmitted to a satellite in space, and will be success full accept back by satellite earth station purposes.
The workings of the transmission of data via satellite by taking into account these components, which receives signals from the satellite earth station (up-link) and then amplify the signal, changing the frequency and re transmits the data to a ground station other recipients (down-link). In satellite transmission at delay or delay for the signal to move into space and back to earth, the lag time of approximately 0.5 second. Satellites use different frequency to receive and transmit data. Satellite frequency range are:
4-6 giga hertz, called the C-band
12-14 giga hertz, called the Ku-Band
20 giga hertz.
Satellite transmission media excellence
Area wide coverage, reach broad scope of national, regional and global, can even reach half of the earth's surface.
V SAT can be mounted anywhere for entry in satellite coverage.
Can be connected anywhere. No need to happen L o S (Line of Sight) and there is no problem with the distance, because the straight line transfer of data to the outside world so it is not obstructed by buildings - building / geographical location of the earth.
Communication can be done either point to point or from one point to many points in broadcasting, multi casting.
Reliable and can be used for voice connections (P A B X), video and data, by providing a wide bandwidth to hire the provider alone.
If the access network to the Internet directly to the ISP / NAP router.
Very good for the area and the sparse population density does not have telecommunications infrastructure.
Satellite transmission media (V SAT) will not collide with other V S A T because it has an orbit of each - each of which is unique, so may not be the same. While in wireless, there could be a collision frequencies with other wireless users or the frequency in the area is already full so having trouble.
Weakness wireless transmission media
To pass the signal T C P / IP, the amount of throughput will be limited due to the propagation delay of geostationary satellites. Now, various techniques link protocol has been developed so as to overcome the problem. Among them the use of Forward Error Correction which ensures a small probability of re transmission.
In terms of security, namely the transmission of data very easily arrested for walking through the open air.
Prices are relatively expensive because the price of expensive equipment.
Takes place, especially for CD / antennae.
The time required from a point on the earth to another point via satellite is about 700 milliseconds (latency), while leased line only takes about 40 milliseconds. This is due to the distance that must be taken by the data that is from the earth to the satellite and back to earth. Geostationary satellites themselves altitude of about 36,000 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
Rainfall is high, higher frequency signals are used, the higher the attenuation due to rainfall. For areas such as Indonesia with high rainfall will use Ku - band satellite link greatly reduces the expected availability. As for the sub-tropical areas with low rainfall will use Ku - Band was excellent. This frequency selection will affect the size of the terminal that will be used by each customer. And also, the satellite transmission medium susceptible to weather, dust meteor / space dust and other weather conditions.
Sun Outage, Sun outage is a condition that occurs when the Earth - satellite - sun are in one straight line. Satellites orbiting the earth in geostationary orbit at geosynchronous were on the equator line or equator (at an altitude of 36,000 Km) regularly and had twice the sun outage annually. Thermal energy emitted by the sun when the sun outage resulted in momentary interference on all the satellite signals, so that the satellite has lost communication with ground stations, both head-end / teleport and ground-segment usual.
Often the hydrazine gas fired (H2Z) so that rotation of the satellites to be stabilized satellite in orbit, the satellite needs calibration several times in order to remain in orbit.
Comparison of wireless and satellite transmission media
Based on the reviews - a review, then look comparisons wireless and satellite transmission media. Weaknesses / advantages of wireless transmission media / satellite is seen from the needs and requirements of customers / one such company, then in terms of network development, the location (geographic location), and the device's other side.
Wireless transmission media is cheaper than satellite transmission medium. Most wireless transmission medium used in connection in public areas and there is also a branch - the branch of the company.
Most media satellite transmission (V SAT) used for connections within large enterprises.
In terms of latency, higher transmission medium satellite its latency in wireless appeal.
Then, satellite did not pay attention to the distance, the distance does not affect, while the short-range wireless data transmission frequency influence.
At the higher wireless radio waves, the higher bandwidth but the distance is getting shorter.
For location, it is not possible to use wireless transmission media around the building or buildings - tall buildings. It impressed not be effective when using wireless transmission medium because it can happen or N LOS N LOS.
In terms of the device used. At satellite direct transmission from the satellite, while the wireless transmission medium depends on the device used (access point, radio links, etc.). On satellite using a hub. In the wireless transmission media, use the device access point (AP) to transmit data, while the satellite transmission medium transmits the data directly from the satellite (V SAT LINK), others use a hub. AP typically has a coverage area of up to 100 meters, which is usually called a cell or range. So to reach (area coverage), satellite transmission media can reach farther than wireless transmission medium. Then, either wireless or satellite transmission medium has a working system with different frequencies.
Depending on the application, the satellite can be used with different designs landline network or network topology. At its simplest, the satellite can support one-way or two-way linking between two earth stations (each called transmission simplex and duplex transmission). More complex communication needs can also be overcome by more advanced network topology such as star and mesh.
microwaves
Microwaves (English: microwave) are electromagnetic waves with super high frequency (Super High Frequency, SHF), which is above 3 GHz (3x109 Hz).
If the microwaves are absorbed by an object, it will appear the warming effect on the object. If the food absorb microwave radiation, heat and cook food to be in a short time. This process is used in a microwave oven.
Microwaves are also used in radar. radar used to locate and determine the trace of an object by microwaves with a frequency of about 1010 Hz.
Physical Description Satellite communication is a microwave relay station. Used to connect two or more transmitter / receiver microwave on earth, which we know with earth station or ground station. Satellite receive a transmission over a single frequency band (up link), amplifies and repeats the signals, plainly transmitting it to another frequency (down link). A single orbiting satellites will operate in several frequency bands, referred to as transponder channel or simply transponder.
High Throughput Satellites (HTS)ViaSat-1 is a kind of High Throughput Satellites (HTS)ViaSat-1 is a kind of High Throughput Satellites (HTS)Transportation ViaSat-1 with Antonov cargo planeTransportation ViaSat-1 with Antonov cargo planeBRIsat launched from the Guiana Space Centre, located in French Guiana. BRIsat satellites are manufactured by Space Systems Loral (SSL) from the United States (US). The satellite carried by Ariane V rocket belonging to Arianespace, the commercial launch of a rocket company owned by the government of France.BRIsat launched from the Guiana Space Centre, located in French Guiana. BRIsat satellites are manufactured by Space Systems Loral (SSL) from the United States (US). The satellite carried by Ariane V rocket belonging to Arianespace, the commercial launch of a rocket company owned by the government of France.
High Throughput Satellite (HTS) is a technology in which data access via satellite capacity could be far greater than the capacity that is currently widely used.
If the current maximum capacity is 155 Mbps Throughput, through technology High Throughput Satellite (HTS), data access speed can reach 100Gbits. Implementation of the system High Throughput Satellite (HTS) can be applied to all types of transponders, such as Ka-Band, Ku-Band and C-Band.
List of high throughput satellites:
Anik F2 (July 2004)
Thaicom 4 (IPSTAR) (August 2005)
Spaceway-3 (August 2007)
WINDS (February 2008)
KA-SAT (December 2010)
Yahsat Y1A (April 2011)
ViaSat-1 (October 2011) [3] [4]
Yahsat Y1B (April 2012)
EchoStar XVII (July 2012)
HYLAS 2 (July 2012)
Astra 2E (September 2013)
O3b satellite constellation (June 2013)
Inmarsat Global Xpress constellation (2014)
Intelsat Epic (2015)
Global Positioning SystemSatellite PositioningSatellite Positioning
Global positioning system [5] (English: Global Positioning System (GPS)) is a system for determining the location on the earth's surface with the aid of alignment (synchronization) satellite signals. This system uses 24 satellites that transmit microwave signals to Earth. This signal is received by a receiver on the surface, and is used to determine the location, speed, direction and time. A similar system with GPS, among others, the Russian GLONASS, Galileo the European Union, IRNSS India.Transponder frequencyAllocation of frequency transponder C-bandAllocation of frequency transponder C-band
Frequencies used for satellite communications are arranged in the form of canals called transponder. One can have a lot of satellite transponders, depending on the design and intended use. For instance, Palapa - D satellite has 40 transponders consisting of 24 C-band transponders, 11 Ku - band transponders and 5 Extended C-band transponders. Total number of transponders is intended to anticipate the needs of customers is increasing.The frequency band is the most popular satellite C-band (4-6 GHz) because signals at this frequency is not affected by the rain and is free of interference signals terrestrial microwave. The allocation of the C-band frequencies are detailed in the figure below, in which the bandwidth of the transponder is capped at 36 MHz and between the transponder given distance (guard band) at 4 MHz (Figure 1b). Figure 1a shows frequency allocation of each of the following transponder center frequency, while images 1c shows the maximum and minimum frequency of a transponder. (In this picture taken transponder examples 7H).
Based on the example in Figure 1c above the maximum frequency of 4200 MHz transponder is 12V, while the minimum frequency of 3700 MHz transponder 1H is. Thus the total frequencies allocated for the entire transponder is 4200 - 3700 = 500 MHz.
While the total number of transponders total of 24, while the bandwidth of each transponder 36 MHz and 4 MHz guard band. It is estimated it will obtain the linear transponder = 24 x (36 + 4) MHz = 960 MHz. That is, to 24 transponders @ 36 MHz and 4 MHz guard band @ required total bandwidth = 960 MHz. But in fact quite the 500 MHz only requirement had been fulfilled. This means we can save bandwidth almost half. This can happen due to inherent polarization waves (electromagnetic) which can be used, namely that the two waves are mutually perpendicular polarization will be isolated from one another. The amount of insulation factor is about 30 dB or trillionth-thousand. with words In other words, the two signals can use the same frequency as long as the different polarization by 90 degrees. By utilizing this phenomenon then we can save bandwidth in half.




Satellite Positioning
Deep Space Network
View from the Earth's north pole, showing the field of view of the main NASA's Deep Space Network antenna locations. Once a mission gets more than 30,000 km from the earth, it is always in view of at least one of the stations.
View from the Earth's north pole, showing the field of view of the main NASA's Deep Space Network antenna locations. Once a mission gets more than 30,000 km from the earth, it is always in view of at least one of the stations.
Deep Space Network is a communications network that supports the mission interplanetary spacecraft; some examples that already exist, such as:
NASA's Deep Space Network
Chinese Deep Space Network
Europe Deep Space Center
Japan Deep Space Center
Indian Deep Space Network
Soviet Deep Space Network

Mission Control Center
The room controllers International Space Station, Russia and the United States.German Space Operations Center, GSOC, OberpfaffenhofenGerman Space Operations Center, GSOC, Oberpfaffenhofen
Mission Control Center or the Mission Control Center (MCC) is the controlling center of the control, monitoring and support activities associated with manned spacecraft flight.earth station
MYK-15A satellite ground stationMYK-15A satellite ground station
Earth station is a telecommunications terminal that is in the earth, which is designed to communicate with the spacecraft or receive radio waves from outer space.
Earth stations are usually built in places far from settlements because "radiation" or dusty industrial area.
Earth Stations (Ground Segment) is part of a satellite transmission system located on Earth and function as a terminal station; namely modifier Base Band signal and / or signal frequency noise, be the signal for the radio frequency, and vice versa. as a terminal station.
At the beginning of the operation, the earth station can be divided into five types, is based on the functionality, capacity and facilities from the ground station concerned. Fifth kinds of earth stations that are:
Master control station,
Great Earth Station,
Medium Earth Station,
Small Earth Station,
Earth Station Mini


International Space Station control room in Russia and in the United States

German Space Operations Center, GSOC, Oberpfaffenhofen
Launch vehicle
In space flight, launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket used to carry a payload from the Earth's surface into space. A launch system including launch vehicles, launch stage platform and other infrastructure. Cargo payload is usually artificial satellites placed into orbit, but some are sub-orbital spaceflights while others allow the spacecraft to get out of Earth's orbit entirely. A launch vehicle that carries a charge on a suborbital trajectory is often called a sounding rocket.
The launch vehicle, launch vehicle orbital particular, have at least two stages, but sometimes up to 4.Rocket upper stagesRocket upper stagesRocket upper stages
Rocket upper stage or upper stage rocket stages alone is over that promotes the charge on the trajectory delivery, or to a higher orbit than the actual orbit that can be achieved using a rocket booster.
Often, the upper stage engine can be restarted back several times in space.
Several stages remain attached to the payload on them and provide a long service after reaching their initial orbit. Many spacecraft early American intelligence, for example, the upper stage Agena remain attached throughout their operational life. Agena spacecraft will provide the strength, communication, and attitude control, as well as providing the required orbital maneuvers.
 MYK-15A satellite ground station
MYK-15A satellite ground station 


remote sensing
Remote sensing, remote sensing (or abbreviated sensing) is a measurement or acquisition of data of an object or phenomenon by a device that does not physically make contact with the object or measurement or acquisition of data of an object or phenomenon by a device remotely, ( eg from aircraft, spacecraft, satellites, ships or other means. Examples of remote sensing include earth-observing satellites, weather satellites, monitor the fetus by ultrasound and spacecraft that monitor the planet from orbit. the sense comes from the English remote sensing, French télédétection, German fernerkundung, Portuguese sensoriamento Remota, Spanish percepción remote and Russian distangtionaya. in modern times, the term remote sensing refers to a technique that involves instruments in the aircraft or spacecraft and distinguished by sensing such as sensing medical or photogrammetry. Although all things related to astronomy is actually the application of remote sensing (remote sensing fact an intensive), the term "remote sensing" more generally to dealing with terrestrial and weather observations.

Rocket upper stages
radio astronomy
Radio astronomy is the branch of astronomy that studies celestial phenomena by measuring the characteristics of radio waves it emits. Radio waves have wavelengths longer than light waves. To get a good signal, radio astronomy antenna need large or small groups of antennas that work simultaneously (for example: the Very Large Array in New Mexico, United States).opals
Opals (Optical Payload for Laser comm Science) is the optical communication in space experiment developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to the International Space Station. It is testing the potential in the use of laser optics to transmit data at a higher level, namely from space-based traditional RF communication, to Earth from space. It was launched to the orbital station on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket on April 18, 2014, as part of an unpressurized cargo spacecraft SpaceX CRS-3 Dragon

Resources Satellite
Every satellite requires power resources. Factors to consider are cost, durability, and effectiveness (the amount of power generated). Satellite spend a lot of electricity. Placement of power resources mounted inside or outside of a satellite.
Some resources for satellite power which may include:
solar panels
battery
nuclear power
heat generators
Radioisotope thermo electric generators
Radioisotope thermoelectric generators or radioisotope thermo electric generator (RTG, RITEG) is an electricity generator that uses an array of thermocouples to convert heat released by the decay of radioactive material that fits into electricity by the Seebeck effect.
RTGS have been used as power sources in satellites, manned spacecraft and remote facilities such as a series of lighthouse established in the Soviet Union within the Arctic Circle.



List of countries with satellite launcher
Countries capable of launching satellites of their own, including the manufacture of launch vehicles.
Note: many countries that can design and construct a satellite which arguably does not require the capacity of the economy, science and industry are high but was not able to launch it, and they are using a foreign launcher. The list below does not put a variety of countries, and just list countries capable of launching satellite's own, plus the date on which the country shows his abilities. Onwards also does not list a satellite or satellite multinational consortium.
The first launch from various countries
| step | state | years | Rocket | Satellite |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1957 | Sputnik-PS | Sputnik 1 | |
| 2 | 1958 | Juno I | Explorer 1 | |
| 3 | 1965 | Diamant | Astérix | |
| 4 | 1970 | Lambda-4S | Ōsumi | |
| 5 | 1970 | Long March 1 | Dong Fang Hong I | |
| 6 | 1971 | Black Arrow | Prospero X-3 | |
| 7 | 1980 | SLV | Rohini | |
| 8 | 1988 | Shavit | Ofeq 1 | |
| — | 1992 | Soyuz-U | Templat:Kosmos | |
| — | 1992 | Tsyklon-3 | Strela (x3, Russian) | |
| 9 | 2009 | Safir-2 | Omid 1 |



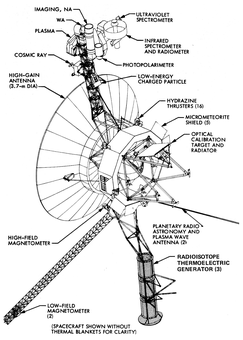
Voyager space diagram



X . IIIII
application of microprocessor system for both satellite and communications hub to hub relations
Almost microprocessor system is widespread in the field of human life, such as education, health, population, politics, war, etc. Some systems used in electronic equipment, including hardware analog systems and digital systems based on microprocessors.
Analog hardware systems are systems that use analog components and complex wiring between the basic components. Deficiencies in both systems is significant that it can not be re-programmed, the tool only for the digital function.system programmable or microprocessor-based system has several advantages:a. The size is small and compact, with many components of this system are reduced existence and replaced with a microprocessor alone.b. Portable, easy to carry anywherec. Low power consumption, since the use of semiconductor materials, IC components no longer require high power for activation and no longer waste large heat.d. Programmable, microprocessor system first advantage is its ability to be reprogrammed in the event of certain changes, so not much to do except change and then memory contents only.e. Low cost, in addition to many of the components are reduced, IC production costs continue to decline so that the overall price of microprocessor-based equipment and then decreased.The use of microprocessor systems are divided into three categories, namely:a. Computer systemb. The communication systemc. Control systems and instrumentation
In the communication system, almost all the important tools in use microprocessor system. The communication system is almost always associated with a computer or microprocessor. Some examples follow:a. Central telephone PSTN or analog channels with a bandwidth of 4 kHz. All systems or telephone lines switching done digitally, random sequential input output or vice versa.b. Digital Telephone Provider such as ISDN, DSL etc. Besides being used for switching or connecting a microprocessor system digital phone provider is also used for many things including optimization of network management and Quality of Service.c. Cell Phone Provider. Although using a radio channel frequency, nearly all cell phones to apply digital communication.d. Satellite communications. Microprocessors are also used for switching, multiplexing, queuing, error correction etc.e. Mobile. Cheap mobile phones are small and must be equipped with a microprocessor.
The use of microprocessor control systems and instrumentation applied to almost all of the instruments and control devices, ranging from small instruments such as bar code readers, to the instrument panel as large as an airplane. Ranging from medical devices to the tools of war. Some examples of the application of microprocessor system for instrument control and instrumentation.a. EFI , electronic fuel injection as applied to modern combustion engines. Ii tool used to optimize the use of fuel for torque and maximum speed.b. System settings print permanence and cut the doubling machine paper media such as newspapers and magazines. Without correction of microprocessor systems, in addition to results that are less tidy, cutlery or printer must often be set back and this is very unrealistic.c. Instruments lifts. The processor is used to read keystrokes and control the movement of the electric motor, so that the lift can be moved in accordance with the keystrokes and quite comfortable for the wearer, not to stop or move suddenly.Examples of applications Microprocessor:
Examples of the use of artificial MSP430F413 Texas Instruments processor for controlling the distance measuring tool that uses ultrasonic waves of 40 kHz. Microprocessors on the device acts as a controller that in active signal receiver or wait for the arrival of the reflected signal, and then calculate the distance between these tools with objects that reflect ultrasonic signals and displays the results of the calculations in decimal numbers on 7 segment display.
It consists of four major components, namely:a. Single chip microprocessor system or in a single chip that contains the processor. Memory and I / O despite the very small capacity.
b. Producing electronic circuits and receiving ultrasonic waves
c. Display 7 segment
d. Program in assembly language that consists of several modules, namely initialization, the reader active button, controlling the sender and receiver, measuring the duration of wave propagation, and the viewer distance calculator to 7 segment
Microprocessor
Satellite communications. In addition to the control and instrumentation system satellites, the microprocessor is also used for switching, multiplexing, queuing, error correction, etc.
Communications satellites are artificial satellites are placed in space with the goal of telecommunications using radio at microwave frequencies. Most communications satellites use geosynchronous orbit or geostationary orbits, although some of the latest type using low Earth orbiting satellites.
Satellite communications function is to provide radio, television, and telecommunications to places on earth.
: MICRO CONTROLLER
"The Clapper" that uses sensors sound of clapping hands to turn on or turn off electronic equipment that exist such as lights and televisions.
The working principle of "The Clapper" itself is using sensors sound of clapping hands manual (clap), which will sound will go through the mic that is embedded in the device which will be processed by a micro controller that is programmed and translate it as an instruction to disconnect or connect the flow electricity in certain electronic devices.
For example, with one pat to turn on or turn off the lights, claps twice to turn on or turn off the television, three times a pat to turn on or off the AC.

satellite carrier rocket