little concept of laser communications
Photo: Laser Light.
Technological developments have shown a significant increase, especially in the area of communication. This is evidenced by the many communications media be it wireless or wired. In this study used light as a medium of communication systems, in addition to the function of light as illumination. In this study realized prototype laser communications system that utilizes light function from the Laser to become a communications system. Prototype laser communications system consists of a transmitter and receiver. The transmitter consists of a laser, audio transformer and batteries. While the receiver consists of a photo diode, amplifier and power supply. The method used in the measurement is a method Line of Sight (LOS) in open channels and closed conduits. The parameters that can affect the results output communication system is within and outside light, because the farther the distance, the smaller the intensity of laser light received receiver.
X . I
Space Communication Switch to laser beam

The laser beam, the light beam converged once considered unsuitable for long-distance communications, the likelihood is the best way to send large amounts of data in space.Scientists at the US National Institute of Standards and Technology and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory - NASA says it has developed a series of small superconducting light sensor is sensitive enough to detect the smallest particles of light - measuring one photon. In fact, the chip can detect the position - left or right, up or down - from every photon that goes into the sensor circuit.Light signals can be coded based on the position of each photon, and also based on the time interval when it is emitted. The researchers say this allows the transfer of volumes of information in a very large number, faster and less costly than using radio - which is currently used for data communication in space.The researchers say the sensors can absorb the data of tens of millions of photons per second, and they expect future versions will be able to process one billion photons per second.In recent trials, scientists use a series of laser sensors to exchange data with NASA spacecraft orbiting the moon six times faster than the best existing radio communications. The researchers said the laser system that weighs half of a radio device and its function is comparable, and use 25 percent less energy.

Space laser communication is a use of lasers for telecommunications in space. This is an application of laser communication and visible light communication.
X . II
bright cloud on LASER

The person who first makes the laser is a physicist called Theodore Maiman in 1960 Maiman using pomegranate-synthetic crystals to create the first laser.Maiman first tinkering with electronic devices in adolescence and even get money to repair the equipment and college radio. He worked at Hughes Research Laboratories air reputable Hughes in Malibu, California, when he built the first working laser.Maiman was nominated twice for the Nobel Prize, but did not win it. He received many other awards before his death in 2007 at the age of 79 years.Lasers are devices which produce coherent light (all lanes in stages) monochromatic (all the same wavelength). Today it is used in eye surgery, dental doctoral, search-range, astronomical measurements, coil (welding) and other refinery use.You will meet them on a scientific instrument, a series of communications, weapons, music system (such as a CD player) and bar code (scanner) supermarket. Lasers are everywhere.



X . III
LASER Diode - How it Works
Laser is very important in optical memories, optical fiber communications, military applications, surgical procedures, a CD player, etc. Various forms of laser printers such as Gallium arsenide laser, Helium Neon laser, carbon dioxide laser, etc. are used in various applications. CD player uses laser technology to read the optical data are recorded in Bits and Pits on CD.
Laser is a narrow beam of photons emitted by the diode laser specially made. Diode lasers are similar to regular LEDs, but produce high intensity light beam. A laser is a device in which the number of atoms vibrate to produce a beam of radiation in which all waves have a single wavelength and are in phase with each other.
laser monochromatic
Monochromatic laser beam and pencil beam can be focused as a typical laser beam has a 4 × 0.6mm widening at a distance of 15 meters. Such as LEDs, laser diodes convert electrical energy into light energy.
Ways of working?
The most common semiconductor laser diode produces laser or injection. In this laser, the population inversion of electrons produced by applying a voltage across the p - n her. The laser beam is then provided on the semiconductor region. The pn junction of the laser diode has polished ends so, the emitted photon reflecting back and forth and create more electron-hole pairs. Photons produced will be in phase with the photons before. It will provide Pencil Beam and all the photons in the beam are coherent and in phase.
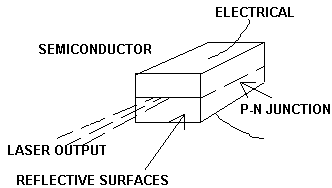
Laser applications
Laser diodes can be switched on and off at a frequency as high as 1GHz, making them ideal in telecommunication applications. Because the laser which produces heat in the tissues of the body hit, it is the ideal solution to cure sensitive parts such as eyes and brain Retina. Lasers can be used to determine the lesion so that the surrounding tissue is not affected as in the case of the operation.
Diode Laser

A bright cloud Attention
Laser is a high-intensity beam penetrates and is very dangerous when focused on the eye. Laser pointer low cost is now available in the market and some people handle them careless and even can give to children to play with. A laser pointer with a higher output power of 5 m W dangerous. Take caution when handling laser diodes. Always take precautionary measures while trouble shooting CD players, laser printers, etc.

X . IIII
Smallest Semiconductor Laser

Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, has gained a milestone in laser physics by creating the world's smallest semiconductor laser and capable of generating visible light in space instead of a single protein molecule. this makes new ground in the field of optics. The UC Berkeley team not only successfully suppress light in a narrow rung, but also find new ways to maintain the light energy from its burst while moving, thereby obtaining the laser action. "This work solves the traditional allegations of laser limits, and makes a large share of applications in the biomedical, communications and computers, Achieving this would help develop an innovation such as nano lasers that can probe, manipulate and characteristic schematic molecule - DNA molecule; optics-based communications several times faster than current technology; and an optical computer in which light replaces electronic circuitry adjusts to the speed leaps and processing power.While it is traditionally acceptable as like as an electromagnetic wave - including laser light - can not be focused beyond the size of half a wavelength, a team of researchers around the world have found a way to compress light under dozens of nano meters to incorporate them in the electrons - electrons which collectively move to and fro on the metal surface. The interaction between light and electrons - electrons move known as surface plasmons.Scientists have been racing - race to construct surface plasmon lasers that can survive and use the optical excitation is very small. However, the nature of resistance However, the metal causes the surface plasmons are scattered almost immediately after the result and have a critical challenge in obtaining enhancer of the electromagnetic field necessary for to be LASER . the researchers took a novel approach to stem the loss of light energy with a pair of cadmium sulfide nano wire - 1,000 times smaller than a human hair - with a silver surface separated by a delimiter gap of only 5 nano meters, the size of a single protein molecule. In this structure, the gap region stores light within an area 20 times smaller than the wavelength. Because light energy is largely stored in non-metallic gap is small, her loss can significantly be reduced. By the end of the loss under supervision until this uniqueness, the design of "hybrid", the researchers can then work on to be amplification of light. "When you work on a small scale, you do not have much space to play - play". "In our design, the nano wire acts as both capping mechanism and an amplifier. This requires double work. "Trapping and support of light in a small space creates an extreme situation in which the interaction of light and the material is very strong change, the author's description of the study. An increase in the spontaneous emission rate of light is a sign pointer from changing this interaction; in this study, the researchers estimate a sixfold increase in the spontaneous emission rate of light in a gap size of 5 nano meters.
New - Recently, researchers from Norfolk State University reported that the actions LASER gold field in a dye-filled, kind of framework of glass embedded on a solution. Double-dyed gold fields could generate surface plasmons when exposed to light.
The UC Berkeley researchers used semiconductor materials and fabrication technologies that are commonly employed in modern electronics manufacturing. By engineering hybrid surface plasmons in the gap between the semiconductor and the metal, they are able to withstand quite a strong light is limited in that its oscillations stabilized into the coherent state that is key on the characteristics of a laser.
"What is particularly exciting about the plasmonic lasers we demonstrated here is that they are solid and highly compatible with semiconductor manufacturing, and then they can be electrically pumped and fully integrated at chip-scale,"
"Plasmon lasers represent a class of activists from the source - the source of coherent light that is capable of the very small restriction in the extreme," said Zhang. "This work can bridge the worlds of electronics and optics on the length scale of the real molecular
Scientists eventually hope to shrink the size of the wavelength of light on the electron, which is about a nano meter, or a billionth of a meter, so that both can work together - together on equal footing.
"The advantage optic - optic in the field of electronics is very much,"
"An example, the equipment will be more powerful and efficient at the same time they give rise speed or bandwidth."
X . IIIII
some examples of how the series of laser communication in daily life
LASER (abbreviation of the English language: Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation)Lasers amplify light. Laser beams of light that can take the weak and make it a powerful beam. Some laser beam produces a very strong so it can burn a small hole in a piece of iron in less than one second.The laser beam can reach long distances through space without spreading and becoming weaker. Therefore, the laser beam into an important communication tool in communicating in an era of outer space. Many uses lasers are found in medicine, science, and industry.Scientists regard the light as a wave moving. The distance from the skin to the skin following a wave of so-called wavelength. Light from the sun or from a lamp is a mixture of many wavelengths. Each different wavelengths produce different colors.The laser beam is made of light that are all composed of the same wavelength. Light beam in ordinary light to flow in a different direction. The laser beam moves in exactly the same direction. The laser beam is not spread out and not weakened
At the beginning of its development, people do not mention the name of the laser. Experts call this time as a maser (Microwave Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of Radiation. And the so-called first revealed masers are Albert Einstein between 1916 - 1917. The famous eccentric scientist who is also the first time found a light or rays not only consists of electromagnetic waves, but also charged particles and energy. and the unknown was what is referred to as radiation. but maser of Einstein is merely a theory. Technology in the second decade of the 20th century has not been able to make it happen. in addition, many scientists who consider Einstein's theory of a controversial theory.In the following years, especially during the second world war, the maser is more widely used for military purposes, namely for the development of radar. Until finally Charles H. Townes, James Gordon and Herbert Zeiger, managed to make maser using ammonia gas. And this is the maser was first created. The success was published in 1954. It is a maser with an energy level. Furthermore, the idea of two levels to maintain emissions at maser inversion has been developed by two Soviet scientists, Nikolai Basov and Alexander Prokhorov. Because this very important contribution in the development of the maser, Charles H. Townes, Nikolai Basov and Alexander Prokhorov shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1964.Charles H. Townes indeed anyone who plays an important role in the world maser. Previously he shared Arthur Schawlow have explored the possibility of making an optical maser (which later evolved into the laser) and infrared rays. Details of the study were published in December 1958. But they were still having trouble and manufacture laser (optical maser). Until the end before entering the 1960 Theodore Maiman can realize a laser beam work. Maiman using Ruby stone cylinder to trigger laser until the laser homemade known as Ruby Laser. But Ruby Laser energy is only able to work on the third level. After entering 1960, Peter Sorokin and Mirek Stevenson began developing the first four-level laser. But it was still a theory and purpose to realize it still has not been reached. However, since it was the laser era began.At first glance that Theodore Maiman considered as the first person to successfully make the laser (not maser). But actually there are others that have preceded it, namely Gordon Gould. In 1958, Gordon Gould reportedly has succeeded in making optical maser (laser) and even he is also regarded as the person who first used the term Laser (Light Amplification by the Stimulated Emission of Radiation). But Gordon failed to register its laser patent in 1959. Until 1977, Gordon won the patent. It took eight years to get recognition.At about the same time are also a few other scientists managed to make a laser using different materials. For example Ali Javan, William Bennett and Donald Herriot makes laser with helium and neon gas media in 1960 and recently published his success in 1961. Kumar N. Patel makes laser through carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium in 1964. And in the year the same is also (1964), Earl Bell makes laser with the help of helium and mercury. Scientists have considered maker for gas lasers because of the materials they use to make the laser is generally a gaseous substance.Fairly important developments occurred in 1962 when a scientist working on a General Electric company, Robert Hall, find the mini-sized semiconductor laser with a low cost. Usually machines or equipment-producing large-sized laser beam. Laser-made Rober Hall is that up to now used on the VCD and DVD players, laser printers, bar code readers, drives the CPU, communication systems using optical fibers, and so forth.A revolutionary discovery made in 1970 when Charles Kao and George Hockham managed to create what is now called optical fibers (fiberglass). They both did not make a laser, but its discovery is very important in the use of laser applications. And as we know, are widely used in fiber optic communication field. The areas that is regarded as the largest user of laser applications. Laser and fiber optics is two discoveries were very mutually supportive.
There are various types of lasers. Laser medium can be a solid, gas, liquid or semiconductors. Laser is usually determined by the type of material used by the amplifierSolid-state laser material has been corroborated distributed in a solid matrix (such as ruby or neodymium: yttrium-aluminum garnet laser yag). Neodymium-Yag laser emits infrared light at 1064 nano meters (nm).Gas laser (helium and helium-neon, HeNe, is the most common gas lasers) has a main output of an infrared lamp. CO2 lasers emit infrared energy offing, and is used for cutting hard materials.Excimer lasers (the name is derived from the terms excited and dimers) use reactive gases, such as chlorine and fluorine, mixed with inert gases such as argon, krypton or xenon. When electrically stimulated, a pseudo molecule (dimer). When lased, the dimer produces light in the ultraviolet range.Dye lasers use complex organic dyes, such as rhodamine 6G, in liquid solution or suspension as the amplifier medium.Semiconductor lasers, sometimes called diode lasers, lasers that are not solid-state. Electronic devices that use is generally very small and use low power. They can be built into a larger array, such as the writing source in some laser printers or CD player.
In everyday life, the laser is used in various fields. In use, the laser energy emitted per unit time is expressed by the order of a few mW (laser block, used in laser disc audio system) up to several MW (Laser used for weapons). The amount of laser energy that is selected depending on its use. Utilization of the laser beam, for example in the fields of medicine, services (services), industrial, astronomy, photography, electronics, and communications.In the field of medicine and health, a laser beam is used among others to diagnose the disease, disease treatment, and repair a defect and surgery.In the industrial field, the laser beam is useful for welding, cutting steel plate, as well as for drilling.In the field of astronomy, high-power laser beam can be used to measure the distance of Earth Month carefully.In the field of photography, lasers capable of producing three-dimensional image of an object, called holography.In the field of electronics, small-sized solid state lasers used in optical memory storage system in a computer.In the field of communications, laser serves to amplify the light that can deliver voice and image signals through optical fibers.
X . IIIIII
Fiber Optic Technology
Fiber optics is a pure glass that is long and thin and the diameter of a human hair. And in its use multiple fiber optic put together in a place called optical cables and used to deliver digital data in the form of light in a very far distance
Core is a thin glass that is a core part of the fiber optic beam delivery which do.
Cladding material surrounding the core is functioning reflects the light back into the core (core).
Buffer Coating is a plastic coating that protects the fiber from damage.
1. Single-mode fibers
core optical fiber with extremely small (0.00035 inch diameter or 9 micron). diameter approaching the wavelength so that the light that goes into it is not reflected-reflective wall cladding.
Fiber Optic Transceiver
2. Multi-mode fibers
optical fiber with a core diameter rather large (diameter of 0.0025 inch or 62.5 microns) were made in it will bounce laser-reflective wall cladding which can lead to reduced bandwidth of the optical fiber type.
How Fiber Optics Work
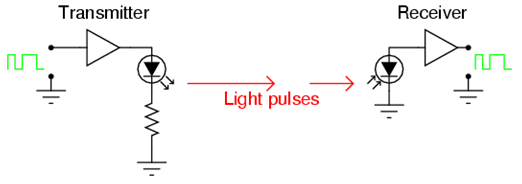
Early signal in the form of electrical signals at the transmitter is converted by the transducer opto electronic (Diode / Laser Diodes) into light waves are then transmitted via fiber optic cable to the receiver / receiver located at the other end, the receiver / receiver optical signal was converted back into electrical signals by transducer Opto electronics (Photo Diodes / Avalanche Photo diode).
But in the course of the optical signal from the transmitter to the receiver so that the light attenuation would occur if the transmission distance is far then needed a repeater to amplify the signal back.
Indoor/Outdoor Tight Buffer
Indoor/Outdoor Breakout Cable
Aerial Cable/Self-Supporting
Hybrid & Composite Cable
Armored Cable
Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH)
outer sheath
In the color coding standardization of outer sheath (jacket) of fiber optic cables Patch Cord types are as follows:
Color
Yellow single-mode optical fiber
Oren multi-mode optical fiber
Aqua Optimal laser micrometer 10 giga 50/125 multi-mode optical fiber
Grey color code optical fiber multi-mode, which is not used anymore
Blue Sometimes they are used in the design model
connectors
Fiber optic cable, the connection terminal ends or also called connectors, usually have a standard type such as FC, SC, ST, LC, or MTRJ. In addition to the connectors typically use a specific color with the intention as follows:
Color
Blue being the most commonly used mainly for single-mode optical fiber.
Green is no longer used for multi-mode optical fiber
Black -
Grey, Beige multi-mode optical fiber
white -
Red Special Use
X . IIIIIIII
LASER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
LASER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
Understanding communication with the light, is not new at all, because since hundreds of years ago, people have found ways to talk remotely using light. In human history, known usage burning torch for the most effective communication tool. Heliogaf gleaming mirrors reflect sunlight so far in high kilo meters is a communication tool that is not a small role. Lighthouse built-island remote island middle of the ocean, is clearly the most important communication tool for the ship that was sailing across the ocean.
The more rapid development of human life also increase the need for the use of telecommunication services from year to year tend to be beyond the capabilities of existing channels.
To accommodate these needs, the world of telecommunications equip its network with a laser beam. With giant channel ability that goes far beyond the needs. A beam of laser light will be able to provide a number of channels to accommodate all types of telecommunications around the globe.
Laser is essentially an oscillator that operates at a frequency of light, the laser only serves as an energy provider of electron flow in the electron tube as usual. As the name implies LASER (Light Amplification by Simulated Emission of Radiation hardening of light by stimulated emission of radiation), Laser stimulates piled radiant energy in the atom itself.
Lasers can form crystals, gas, liquid, and semiconductor each have their own characteristics with a particular user. The crystal type screen, for example, is a kind of stone, ruby red (ruby) can operate at very steeper output power in mega watt (MW). Laser types of gas and liquid form requires low power supply of 10 to 20 watts
Laser gases and crystals as the main supporter of the laser system that is widely used in various purposes. Given the quality of the laser is so high, its use is increasingly up especially in the fields of industry biology , physics, optics and communication. This quality is based on its ability output to coherent beam (solid blend with the same properties). This is precisely what is especially attractive communication experts who want to get a new transmission media for improved distribution of information on a large scale.
transmitterTransmitter consists of 2 parts:
Electrical circuit serves to convert digital signals into analog signals, then the data is superimposed into optical signals that have been modulated wave
Sources of optical waves in the form of rays Laser Diode (LD) and LED ( light emmiting diode) that is adapted to the use of communication necessary.
Laser Diode can be used for optical communication systems are very much like the Cable Communication System (SKKL) and Systems Optical Fiber Communication (SKSO), because the laser LD has characteristics that are reliable that can transmit power with high intensity, stable, almost monochromatic, focused , and spread at breakneck speed, so it can be a great distance. Its manufacture is very difficult because it requires certain specifications so that the price is expensive. So LD uneconomical and inefficient when used for short range communications system and the traffic less congested.
LEDs are used for medium-range communication systems and close so that the system can be an economical and effective because it is easier to make its . LED, so the price is cheaper. LED components necessary to analyze a network that is the emission wavelength, spectral line width, power output, area effective radiation, emision spectrum, and the number of emitting modes.
Can be illustrated the transfer characteristics of LD and LED with analyze it is that once a certain price is exceeded, with the same input turns LD output power is far greater than the LED.
Transmission characteristics
The nature of information transmission can be explained as follows:
The information will be transmitted in the form of data in digital form, while the form of the carrier signal carrier will pass through optical fiber transmission medium in the form of analog signals.
It is necessary for modulation and demodulation process is a process that converts digital data into analog and also the reverse process by using a modem with its appliances.
In this type of optical fiber used as the transmission medium is a graded index multi mode optical fiber.
Laser Beam Systems
The nature of information transmission can be explained as follows:
The information will be transmitted in the form of data in digital form, while the form of the carrier signal carrier will pass through optical fiber transmission medium in the form of analog signals.
It is necessary for modulation and demodulation process is a process that converts digital data into analog and also the reverse process by using a modem with its appliances.
In this type of optical fiber used as the transmission medium is a graded index multi mode optical fiber.
Laser Beam Systems
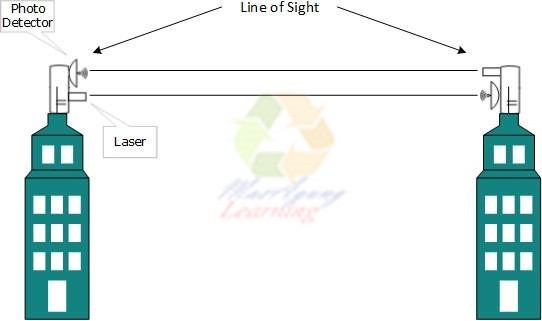
Communication technology is widely used laser light to places far away. Communications experts predict, the future use of laser technology will be expanded and will reduce the cost transmission . but Thus, this technology also has the property line of sight, so if obstructed, then the flow of data and information will be stalled.In the future, this technology will be used by companies that have a building area so media transmission used to connect between building one for the other building systems use laser light.
Laser light
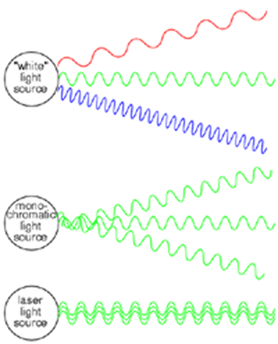
In general, the light we see is a mixture of different wavelengths, or colors are different. Because the atoms are usually issued randomly light, the light waves generated is also not in unison. Two of these factors mean that the ordinary light is a mixture of different types of waves. However, the laser light is different. The laser light does not contain a lot of waves, but only one wavelength. Not only that, the wave-propagation also "coherent", which means that the waves were exactly or rhythm. The laser light is made by filling a solid, liquid, or gas with energy. When an energy-absorbing elements, the atoms begin to release the light at specific wavelengths. If the light from one atom of the atoms of adjacent edges, more light at liberated. This chain reaction continues until many atoms emit light, all at the same time. If the light reflected by the mirrors specifically so that the light was moving backward and forward in the laser over time, the light becomes so intense that a portion of it through one of the mirrors and laser beam shaping.
At Laser Beam TransmissionLASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Lasers can produce coherent light and high intensity. The laser beam can be deflected by using optical devices such as mirrors, prisms, and lenses. The transmission medium is a medium that can be used to transmit information from one place to another. In the network, all media that can channel electricity or electromagnetic waves or light, can be used as a media sender, both for sending and receiving data. The components are selected to meet a network analysis on a diode laser that is the emission wavelength, spectral line width, power output, the effective radiation area, emission spectra, and the number of emitting modes.
Point the laser pointer to one side of the upright on the prism
Prisma is a clear substance that is bounded by two flat areas. When a beam of dating on one of the fields referred to as field refracting prism I, will be refracted approaching normal line. Until the field of refractory II, the light beam will be refracted away from the normal line. In the field of refractory I, rays refracted approaching normal lines, for dating beam from substance to substance less dense optic optic is more dense air into the glass. In contrast in the field of refractory II, the beam is refracted away from the normal, because the light comes from substance to substance optic optic meeting that is less dense than glass into the air. So that a beam of light passing through a prism will experience a deflection direction from its original direction.
Laser light properties including to monochromatic. When the laser beam is imposed on the prism, the laser beam will be refracted by the spread in only one direction. While on the other light rays when worn on the prism will experience light dispersion, which decomposes white light into a rainbow of colors like red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet, called poly chromatic light.
Transmission in the mirrorTo control the light emission of the laser beam, then can be used help of a mirror. Where two mirrors are placed at both ends of a crystal or rubies and one of them made half - silvered (just reflect some light , while light that is not reflected can bust out. Stone ruby stimulated energy (irradiated with light) so that some of the excited electrons . Then the excited electron is trying to energy levels beginning with the release of light (photons). the light is bounced on the surface of the mirror and irradiate the electrons beside causing for excitation at of the electron. Some of the light managed to bust out of the half - silvere mirror. rays a beam of monochromatic, coherent and singular. mirror causing losses in transmission due to diffraction mirror can extend the reflectance of light, where two flat mirrors should be located in parallel and aligned so very accurately to avoid the rays leave the middle of the mirror.
Transmission On Lenses
The lens on the laser beam is useful for focusing the light reflected by the mirror. Two identical lenses that are used to make beams in laser to diversion will spread. Lenses must keep both light devices remain in one phase, in other words exactly in unison or in tune. Laser light beam will split. Files that highlights objects molecule then a lens and is reflected towards it. Reference light beam passing through a lens and can be reflected toward the emulsion photographs and there was met with the reference light from the light highlighting objects .
