MARIA PREFER for load control to be reactive and efficient
so that we can classify the signal instrumentation signals and the number of moving charges in order:
1. ANIANO (Analog Input and Analog Output) = Kilo ampere - Ampere
2. DIGIDIGO (Digital Input and Digital Output) = milli amperes - micro ampere
3. ANIDIGIDIGOANO (ANI___ Processing (DIGIDIGO) ___ ANO)
4. ANIDIGIPHOTONICSDIGOANO (Optic Processing)
Lux processing intensity
Analog signal 0- 20 mA and for Kilo Ampere - Ampere power
digital signal in the form of pulses with a voltage of 0 and 1 that can be 5V, 12 V, 24 V, 36 V.
photonics signals are the number of grids in the luminous or luminous lumens and lux matrices.
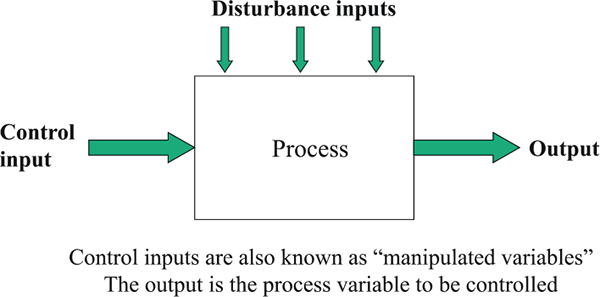
input is a signal that goes into the control loop while output is a signal that comes out of the control loop in the sense that the word control loop is an important component and structure in controlling and conditioning the signal so that the process and display can show modern momentum .
________________________________________________________________________________
CONTROL LOOP AMPERE


________________________________________________________________________________
CONTROL LOOP mili Ampere

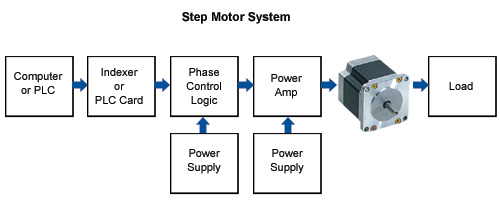
Stepper Motor Working Principle
Stepper Motors works in different "Step Modes" which includes Full Step, Half Step and Micro Step and Wave Drive. The type of step mode output of any stepper motor is dependent on the design of the driver.
Stepper Motors Working with FULL STEP (2 Phases On)
Standard Hybrid Stepping motors have 200 rotor teeth, or 200 full steps per revolution of the motor shaft. Dividing the 200 steps into the 360° of rotation equals a 1.8° full step angle. Normally, full step mode is achieved by energizing both windings while reversing the current alternately. Essentially one digital pulse from the driver is equivalent to one step.
Stepper Motors Working with HALF STEP (1-2 Phases On)
Half step simply means that the step motor is rotating at 400 steps per revolution. In this mode, one winding is energized and then two windings are energized alternately, causing the rotor to rotate at half the distance, or 0.9°. Although it provides approximately 30% less torque, half-step mode produces a smoother motion than full-step mode.
Stepper Motors Working with MICRO STEP
Microstepping is a relatively new stepper motor technology that controls the current in the motor winding to a degree that further subdivides the number of positions between poles. Some microstepping drives are capable of dividing a full step (1.8°) into 256 microsteps, resulting in 51,200 steps per revolution (.007°/step). Microstepping is typically used in applications that require accurate positioning and smoother motion over a wide range of speeds. Like the half-step mode, microstepping provides approximately 30% less torque than full-step mode.
Stepper Motors Working with WAVE DRIVE
In this drive method only a single phase is activated at a time. It has the same number of steps as the full step drive, but the motor will have significantly less than rated torque. It is rarely used.
Components of a Stepper Motor System
A stepper motor system consists of three basic elements; Indexer , Driver and a Step Motor.
Indexers
- The indexer (or controller) is a microprocessor capable of generating
step pulses and direction signals for the driver. In addition, the
indexer is typically required to perform many other sophisticated
command functions.
Drivers - The driver (or amplifier) converts the indexer command signals into the power necessary to energize the motor windings. There are numerous types of drivers, with different voltage and current ratings and construction technology. Not all drivers are suitable to run all motors, so when designing a motion control system the driver selection process is critical.
Stepper Motors - The stepper motor is an electromagnetic device that converts digital pulses into mechanical shaft rotation. Advantages of step motors are low cost, high reliability, high torque at low speeds and a simple, rugged construction that operates in almost any environment. The main disadvantages in using a stepper motor is the resonance effect often exhibited at low speeds and decreasing torque with increasing speed.
Stepper Motor Technologies
-Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor:
It uses a permanent magnet to operate. It is a low cost and low
resolution motor. It also exhibits better torque characteristics than
other types of motors.
-Variable-Reluctance:
This is most easy to understand and most old form of stepper motor. It
consists of rotor teeth that become magnetized when attracted to
energized stator poles.
-Hybrid Stepper Motor:
It is more costly than any other type of stepper motor and also it
yields the best results. It combines the best features of both PM and VR
motors to operate. It has teeth rotor like VR and magnet just like
permanent magnet step motor.
________________________________________________________________________________
Control Loop Mikro ampere -- nano Ampere

_________________________________________________________________________________
CONTROL LOOP PHOTONICS CURRENT
An Optical Phase-Locked Loop Photonic Integrated Circuit :
The design, fabrication, and results from the first monolithically integrated optical phase-locked loop (OPLL) photonic integrated circuit (PIC) suitable for a variety of homodyne and offset phase locking applications. This InP-based PIC contains two sampled-grating distributed reflector (SG-DBR) lasers, semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs), phase modulators, balanced photodetectors, and multimode interference (MMI)-couplers and splitters. The SG-DBR lasers have more than 5 THz of frequency tuning range and can generate a coherent beat for a wide spectrum of frequencies. In addition, the SG-DBR lasers have large tuning sensitivities and do not exhibit any phase inversion over the frequency modulation bandwidths making them ideal for use as current controlled oscillators in feedback loops. These SG-DBR lasers have wide linewidths and require high feedback loop bandwidths in order to be used in OPLLs. This is made possible using photonic integration which provides low cost, easy to package compact loops with low feedback latencies. In this paper, we present two experiments to demonstrate proof-of-concept operation of the OPLL-PIC: homodyne locking and offset locking of the SG-DBR lasers.
LASER DIODES
Laser diodes drivers are electronic devices which are used to supply one or several laser diodes with the required electrical drive current. Most of them obtain electrical power from the public grid, but there are also battery-operated devices.
Basic Functionality
Note that the drive current and not the voltage determines the rate with which electrical carriers are injected into the junction of the laser diode. Therefore, the optical output power is strongly linked to the drive current and less directly to the drive voltage.
For preventing damage of a laser diode, it is important to avoid any excessive drive currents; even short current spikes could destroy a laser diode, e.g. in the form of catastrophic optical damage due to excessive optical intensity as the diode's output facet. Particularly if a laser diodes driver is not made for diodes with a specific maximum drive current, it should have a separate control where the maximum drive current can be adjusted, and the limit set there should be respected by any other controls, e.g. the one which is regularly used to adjust the drive current. (When the current limit is reached, the current may either be clamped to the limit value or switched off until the user reactivates the device e.g. by pushing a button.) In that way, one can greatly reduce the risk that a user accidentally draws the power knob too far; special care has to be applied only when the current limit is set.
In some cases, laser diodes are intentionally overdriven, i.e., operated with a drive current above the recommended maximum. In that way, one may achieve an increased output power, but at the cost of a reduced laser lifetime, and possibly even with the risk of instant damage.
Obviously, a laser diode driver should be relatively immune against external influences such as voltage spikes on the electrical grid or current transients resulting from faulty electrical contacts.
Different Power Levels
Laser diodes and therefore also laser diodes drivers are available in a very wide range of powers.
Some low-power diodes require drive currents of only e.g. 20 mA, whereas high-power diode bars
may be operated with drive currents of dozens of amperes.
In case of high-power diode drivers, it is of interest to have a
switching power supply and related control electronics with high power
conversion efficiency – not only in order to save electricity, but also
to limit the amount of waste heat which normally needs to be dissipated
with additional means such as a ventilator or a water cooling system.
If the system contains multiple laser diodes, one in principle use a separate driver for each one. However, as long as independent power control of these diodes is not required, it is simpler, more convenient and more economical to operate multiple diodes with a single diode driver. Usually, the laser diodes are connected in series, since this guarantees that they are all operated with the same drive current; if they would be connected in parallel, the hottest diode may consume the largest part of the current and thus become even hotter. Also, parallel connections could lead to excessive drive currents in the electrical cables and connectors, also to a reduced efficiency of the driver, whereas higher voltages are often not a problem. For cases with a very large number of laser diodes, one may group the diodes into packages where there is a serial connection of the diodes within each package, and the different packages are driven by separate output stages of the driver (with separate current stabilization). Obviously, the via ring of the used laser diodes (e.g. common cathode or common anode) must fit to the connections of the used laser diode driver.
It is often advisable not to use a laser diode driver which is designed for a much higher drive current than required. Even if a proper current limit can be set, the accuracy of the set operation current may otherwise be worse, the current noise may be higher, and the transient protection may be not sufficiently sensitive for a low-power diode.
If the system contains multiple laser diodes, one in principle use a separate driver for each one. However, as long as independent power control of these diodes is not required, it is simpler, more convenient and more economical to operate multiple diodes with a single diode driver. Usually, the laser diodes are connected in series, since this guarantees that they are all operated with the same drive current; if they would be connected in parallel, the hottest diode may consume the largest part of the current and thus become even hotter. Also, parallel connections could lead to excessive drive currents in the electrical cables and connectors, also to a reduced efficiency of the driver, whereas higher voltages are often not a problem. For cases with a very large number of laser diodes, one may group the diodes into packages where there is a serial connection of the diodes within each package, and the different packages are driven by separate output stages of the driver (with separate current stabilization). Obviously, the via ring of the used laser diodes (e.g. common cathode or common anode) must fit to the connections of the used laser diode driver.
It is often advisable not to use a laser diode driver which is designed for a much higher drive current than required. Even if a proper current limit can be set, the accuracy of the set operation current may otherwise be worse, the current noise may be higher, and the transient protection may be not sufficiently sensitive for a low-power diode.
Additional Functionality
Beyond the mentioned basic functionality, laser diodes drivers can offer a number of additional functions:
Interlock Systems
Very often, a diode driver has some interlock system, which can
switch off the laser in case that a certain safety condition is detected
– for example, and opened device housing.
It can be very useful to have multiple interlock connections for
implementing advanced safety features.
Some of them may treat conditions like insufficient coolant flow on a
chiller in order to avoid hardware defects.
Constant Power Mode
There are devices which can stabilize the optical output power (constant power mode), based on a signal from the photodetector, which may be integrated into the laser diode package.
(That is particularly often the case for fiber-coupled laser diodes.)
Of course, a certain maximum drive current must never be exceeded;
otherwise, a laser diode could be killed as a result of a faulty
photodetector signal.
Often, it is possible to switch between constant current mode and
constant power mode.
Electrical Monitoring Outputs
There may be electrical outputs, e.g. delivering a voltage
proportional to the laser diode current or the monitored optical power,
possibly with a calibration feature.
Protective Features
The applied voltage should be monitored, and if an unusual operation
voltage is detected, the device may switch off the diode in order to
prevent damage.
If several laser diodes are operated in series, a sudden drop of the
voltage may indicate the death of one of the diodes, and it may then be
wise to investigate the situation before the other laser diodes are also
destroyed.
Also, it is useful if the driver recognizes wrong poling of a diode,
because it could be destroyed by an excessive reverse voltage.
For transient protection, the diode's cables should not simply be disconnected when switched off, but rather electrically connected together (shorted), so that electrostatic discharges cannot build up a voltage across the pins.
For transient protection, the diode's cables should not simply be disconnected when switched off, but rather electrically connected together (shorted), so that electrostatic discharges cannot build up a voltage across the pins.
Temperature Control and Monitoring
Some devices have an integrated temperature controller, driving e.g. a
Peltier element based on the signal of some temperature sensor.
Even without a temperature stabilization feature, it can be useful to
monitor the junction temperature for switching off the laser before it
gets too hot.
Alternatively, one may monitor the emission wavelengths, which reacts
sensitively to temperature changes, unless an optical wavelength
stabilization is used, e.g. based on optical feedback from a volume Bragg grating.
Also, it is sensible to monitor the internal temperature of the electronic driver device, since overheating e.g. due to a blocked air or water flow may destroy the driver and possibly the laser diode(s) in addition.
Also, it is sensible to monitor the internal temperature of the electronic driver device, since overheating e.g. due to a blocked air or water flow may destroy the driver and possibly the laser diode(s) in addition.
Low-noise Operation
Some drivers are made for operation with a particularly low current noise.
This can be important, for example, when driving lasers for sensitive optical measurements.
Low-noise operation is mostly offered for low-power devices.
Slow Start Feature and Turn-on Delay
Particularly for high-power laser diodes, it can be useful to limit the rate with which the current can be ramped up and down (slow start feature),
because this reduces the internal mechanical stress related to
temperature changes.
In addition, a turn-on delay is often used as a safety feature; people
in the room are warned about coming laser radiation before it is
actually turned on.
Wavelength Tuning
Some diode lasers, in particular external-cavity diode lasers, are suitable for wavelength tuning in a substantial range.
For example, a diffraction grating on a motorized stage can be used for controlling the emission wavelength.
Some laser diodes drivers contain functionality for tuning the wavelength e.g. via controlling some stepper motor.
Quasi-continuous Wave Operation
Some drivers are suited for quasi-continuous-wave operation (QCW mode).
This means that they can apply current pulses with an adjustable
duration e.g. between 1 μs and 10 ms, which can be triggered with an
external electric signals or with a built-in clock.
The possible peak current may be well above the current which the driver
could deliver continuously, or which the laser diode could tolerate
continuously.
Short and Ultrashort Pulse Generation
They are specialized drivers for producing nanosecond or picosecond pulses, e.g. by gain switching.
Here, it is particularly important to select a suitable laser diode and
to properly adjust the parameters of the applied current pulses.
Current Modulation
In other cases, a laser diode driver allows some other kind of modulation of the supplied current.
This can be done in many different forms.
For example, a TTL input signal may be used to switch the current on or off.
In other cases, an analog input signal is added to the base current set with the controls.
Drivers can differ very much in terms of modulation bandwidth and depth of modulation.
Current modulation is often available only in current control mode, i.e., not in combination with output power stabilization. This is because the limited feedback bandwidth of the stabilization circle it would strongly limit the possible modulation bandwidth.
Current modulation is often available only in current control mode, i.e., not in combination with output power stabilization. This is because the limited feedback bandwidth of the stabilization circle it would strongly limit the possible modulation bandwidth.
Computer Control
A diode driver may be computer-controlled, connected e.g. via a USB,
GPIB or a serial interface like RS-232.
It may receive inputs, e.g. concerning the requested drive current, and
deliver outputs, e.g. concerning the achieved optical output power or
the required diode voltage.
Different Types of Diode Drivers
Some laser diodes drivers are made as instruments specifically for
use in laboratories.
Here, the user usually has direct access to the device and its controls,
which usually include various knobs, buttons and switches, e.g. for
adjusting the diode current or temporarily switching it off.
Laboratory diode drivers usually have a front panel with a digital
display for the diode current, possibly also for other quantities like
the applied voltage or the diode temperature, if the latter can be
measured with a built-in temperature sensor.
Such devices are often not built for a specific type of laser diode, but
with increased flexibility for using different diodes.
This implies that different maximum voltages and currents can be
applied.
Some devices have a standardized housing for mounting in a rack, where they can be combined with other electronic devices.
Finally, there are driver modules for integration into other devices (e.g. mounted on a chassis heat sink) and sold as OEM packages, if not produced by the manufacturer of the system. They often have only electronic interfaces for interaction with other parts of the system electronics, and not directly with the user of the laser device. They are often used in larger quantities and available at lower prices.
Some devices have a standardized housing for mounting in a rack, where they can be combined with other electronic devices.
Finally, there are driver modules for integration into other devices (e.g. mounted on a chassis heat sink) and sold as OEM packages, if not produced by the manufacturer of the system. They often have only electronic interfaces for interaction with other parts of the system electronics, and not directly with the user of the laser device. They are often used in larger quantities and available at lower prices.
Further Remarks
Laser diodes are generally not suitable for “hot plugging”: they
should be connected or disconnected only while the diode driver is
switched off, and proper precautions have to be taken to avoid damage by
electrostatic discharge (ESD).
For example, one may shorten the pins at the diode before disconnecting
the wires from the driver.
Before using a diode driver within some larger system, one should check whether problems could arise due to improper grounding. Some diode drivers have one output pin connected to the case and to earth ground, and may then interfere with additional grounding on other devices. Even if the same pin is connected to earth ground at different locations, problems may result due to a “ground loop” in which magnetic fields can induce disturbing currents.
RPMC LasersBefore using a diode driver within some larger system, one should check whether problems could arise due to improper grounding. Some diode drivers have one output pin connected to the case and to earth ground, and may then interfere with additional grounding on other devices. Even if the same pin is connected to earth ground at different locations, problems may result due to a “ground loop” in which magnetic fields can induce disturbing currents.
RPMC Lasers offers a wide range of laser diode drivers for CW, QCW, and pulsed operation. We offer turnkey laboratory laser drivers, rack-mountable laser drivers, and board level OEM drivers with currents ranging from 100 mA to 300 A. Additionally, the pulsed driver boards are capable of producing transform limited pluses down to 250 ps.
TOPTICA Photonics
Apart from a well-engineered optomechanical design and the integrated laser diode, the most important part of a tunable diode laser system is its driving electronics, which is responsible for getting the most out of a laser system.Wide mode-hop-free tuning with Littrow setups requires a well-defined interplay between piezo actuator and current driver. Drifts of the laser diode current, the temperature or the piezo voltage determine the drift of the laser frequency and the stability against mode-hopping. Noise on any of these outputs increases the laser linewidth. The digital DLC pro represents the latest stage of development of laser control electronics. Its noise and drift properties are even better than the well established and widely used preceeding electronics SYS DC 110.
EKSMA OPTICS
EKSMA Optics offers uniLDD universal laser diode drivers. uniLDD is a DC input power converter designed to supply CW or pulsed current for single emmiter, bar or stacked laser diode in constant current (CC) mode. Drivers can be supplied for a wide current range as well as wide diode compliance voltage range.APIC
APIC produces a turnkey tabletop laser drive module specifically designed to operate its high power, ultra low RIN lasers. The OEM laser of choice is integrated into the laser drive module at the factory. The laser drive module includes a high-quality laser driver with a low-noise power source, current driver and accurate temperature control circuit to maintain stable laser output with minimal noise. APIC is in the process of developing a similar turnkey driver module for its Direct Modulated Lasers (DML).A high-quality laser driver with a low-noise power source, current driver and accurate temperature controls is required. If you do not have such equipment, we recommend you consider purchasing our turnkey tabletop CW laser drive module. The drive module has power conditioning with laser and TEC control electronics designed specifically to operate our lasers with minimal noise.
General optics
 Abbe number
Abbe numberABCD matrix
aberrations → optical aberrations
absorbance
absorbing coatings → black coatings
absorptance
absorption
absorption coefficient
absorption length
absorptivity → absorptance
achromatic lenses → lenses
achromatic optics
adjoint modes → resonator modes
afocal optical systems
aluminum mirrors → metal-coated mirrors
anamorphic prism pairs
anamorphic prisms → prisms
anomalous dispersion → dispersion
aperture stops
apochromats → achromatic optics
aspheric lenses → aspheric optics
aspheric optics
astigmatism
attenuation coefficient → absorption coefficient
axial modes → resonator modes
ball lenses
beam collimation → collimated beams
beam collimators
beam diameter → beam radius
beam distortions → beam quality
beam divergence
beam expanders
beam focus → beam waist
beam homogenizers
beam parameter product
beam propagation factor → M2 factor
beam quality
beam quality factor → M2 factor
beam radius
beam splitters
beam viewing cards → laser viewing cards
beam waist
beat length → polarization beat length
Beer–Lambert law
birefringence
birefringent polarizers → polarizers
black coatings
Bragg gratings
Brewster plates
Brewster windows
Brewster's angle
brightness
cardinal points
caustic → beam quality
cavities
cavity bandwidth → resonator modes
cavity modes → resonator modes
cavity resonances → resonator modes
chirped mirrors
chromatic aberrations
chromatic dispersion
circle of confusion → imaging with a lens
cleaner cavities → mode cleaners
cleaning of optics
coherence
coherence function → coherence time
coherence length
coherence time
collimated beams
collimation optics → collimated beams
coma → optical aberrations
complex degree of temporal coherence → coherence time
complex reflection coefficient → reflectivity
complex refractive index → refractive index
condensers
confocal parameter → Rayleigh length
constringence → Abbe number
corner cube prisms
custom optics
cylindrical lenses
D4σ method → beam radius
deformable mirrors
delay lines → optical delay lines
demagnification → magnification
depth of field
depth of focus
detector cards → laser viewing cards
diameter–divergence product
diameter of laser beam → beam radius
diattenuation → dichroism
dichroism
diffraction
diffraction gratings
diffraction-limited beams
diffractive beamsplitters → diffractive optics
diffractive lenses → diffractive optics
diffractive optics
diffuse scattering → scattering
diopters → dioptric power
dioptric power
dispersion
dispersion relations → Kramers–Kronig relations
dispersive delay lines → optical delay lines
dispersive mirrors
dispersive spectral analysis → spectrometers
divergence angle → beam divergence
domes → optical domes
double-chirped mirrors → chirped mirrors
double refraction → birefringence
dynamically unstable resonators → unstable resonators
effective Rayleigh length → Rayleigh length
elastic scattering → scattering
emission spectrum → optical spectrum
emissivity
entangled states → photons
entrance and exit pupil
exit pupil → entrance and exit pupil
extinction ratio → polarization of light
f–theta lenses → scanning lenses
f-number
f-stop number → f-number
Faraday isolators
Faraday rotators
fast light → superluminal transmission
faster than light → superluminal transmission
field curvature → optical aberrations
field stops
first surface mirrors
flat-top beams
fluence
focal distance
focal length
focal points and focal planes
focus → beam waist
focusing power → focal length
Fourier optics
free-space modes → modes
Fresnel equations
Fresnel lenses
Fresnel number
Fresnel reflections
front surface mirrors → first surface mirrors
Gaussian beams
Gaussian optics
geometrical optics
gold mirrors → metal-coated mirrors
Gouy phase shift
gradient-index filters → rugate filters
gradient-index lenses
gratings → diffraction gratings
group delay
group delay dispersion
group index
group refractive index → group index
group velocity
group velocity dispersion
guided modes → modes
half-wave plates → waveplates
hand lenses → magnifying glasses
heat radiation → infrared light
Hermite–Gaussian modes
higher-order dispersion → dispersion
higher-order modes
holography
hyperfocal distance
image distortion → optical aberrations
image planes
image space → object and image space
imaging
imaging with a lens
index matching fluids
index of refraction → refractive index
inelastic scattering → scattering
infrared absorption → absorption
infrared detector cards → laser viewing cards
infrared light
infrared optics
infrared sensor cards → laser viewing cards
insertion loss
instantaneous frequency
intensity → optical intensity
intermediate image planes → image planes
irradiance
k vector → wave vector
Kramers–Kronig relations
laser beam quality → beam quality
laser beams
laser diode collimators
laser light
laser line optics
laser line polarizers → thin-film polarizers
laser optics
laser radiation → laser light
laser speckle
laser viewing cards
lateral modes → higher-order modes
law of Snellius → refraction
left-handed metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
lens arrays → microlens arrays
lens speed → f-number
lenses
light absorption → absorption
light intensity → optical intensity
linear absorption → absorption
linear polarization → polarization of light
linear polarizers → polarizers
loupes
M2 factor
magnification
magnifying glasses
manufacturing of optics → optical fabrication
metal-coated mirrors
metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
microcavities → cavities
microlens arrays
microlenses
mirrors
mm mrad → beam parameter product
mode cleaners
mode matching
modes
monochromatic light
monochromators
monochromators → spectrometers
near field and far field
negative-index materials → photonic metamaterials
neutral density filters
Nipkow discs → pinholes
nodal points
normal dispersion → dispersion
numerical aperture
object and image space
objective lenses → objectives
objectives
optical aberrations
optical absorption → absorption
optical breadboards
optical cavities → cavities
optical delay lines
optical density
optical domes
optical fabrication
optical flats
optical fluence → fluence
optical frequency
optical images → imaging
optical imaging → imaging
optical intensity
optical isolators → Faraday isolators
optical materials
optical mirrors → mirrors
optical phase
optical power
optical retardance → retardance
optical return loss → return loss
optical slits
optical spaces → object and image space
optical spectrum
optical spectrum analyzers
optical tables
optical thickness
optical wavelength → wavelength
optical windows
optics
optics cleaning → cleaning of optics
optics for lasers → laser optics
opto-mechanics
parabolic mirrors
parasitic absorption → absorption
paraxial approximation
phase → optical phase
phase coherence → coherence
phase velocity
photometry
photonic metamaterials
photons
physical optics → wave optics
pinholes
plane waves
plastic optics
plate beam splitters → beam splitters
polarization beam combining
polarization beat length
polarization coupling → polarization beam combining
polarization extinction ratio → polarization of light
polarization of light
polarization rotators → Faraday rotators
polarizers
polarizing beam splitters → polarizers
polarizing cubes → thin-film polarizers
Polaroid filters → polarizers
polychromatic light
polymer optics → plastic optics
power splitters → beam splitters
principal dispersion
principal points and principal planes
prism-based beam expanders → anamorphic prism pairs
prism pairs
prism retroreflectors → prisms
prisms
propagation losses
protected metal-coated mirrors → first surface mirrors
pupils → entrance and exit pupil
q parameter → Gaussian beams
quarter-wave plates → waveplates
quasi-monochromatic light → monochromatic light
radiance
radiant energy
radiant flux
radiometers → radiometry
radiometry
radius of laser beam → beam radius
ray optics → geometrical optics
ray transfer matrix → ABCD matrix
Rayleigh length
Rayleigh scattering
references surfaces → optical flats
reflectance
reflection coefficient of an interface → Fresnel equations
reflectivity
refraction
refractive index
refractive index fluids → index matching fluids
residual absorption → absorption
resonator bandwidth → resonator modes
resonator modes
retardance
retarders → retardance
retroreflecting prisms → corner cube prisms
retroreflectors
return loss
rod lenses
rugate filters
scanning delay lines → optical delay lines
scanning lenses
scanning spectrometers → spectrometers
scattering
second-order dispersion → group delay dispersion
Sellmeier formula
sensor cards → laser viewing cards
sheet polarizers → polarizers
silicone optics → plastic optics
silver mirrors → metal-coated mirrors
slow light → velocity of light
Snell's law → refraction
spatial coherence → coherence
spatial filters → mode cleaners
spatial frequencies → Fourier optics
speckle → laser speckle
spectral beam combining
spectral lines
spectral radiance → radiance
spectrographs
spectrometers
spectrophotometers
spectroradiometers → spectrometers
spectrum → optical spectrum
speed of light → velocity of light
spherical aberrations
standard spectral lines
super-black coatings → black coatings
superluminal transmission
telecentric lenses
telescopes
TEM modes → resonator modes
temporal coherence → coherence
thin-film polarizers
top-hat beams → flat-top beams
transmission loss → insertion loss
transmissivity
transmittance
transverse modes → higher-order modes
trihedral prisms → corner cube prisms
ultraviolet absorption → absorption
ultraviolet light
ultraviolet optics
unstable resonators
UV-enhanced aluminum mirrors → first surface mirrors
V number of a dispersive material → Abbe number
vacuum velocity of light → velocity of light
vacuum wavelength → wavelength
vacuum windows → optical windows
velocity of light
waist radius → beam waist
wave optics
wave vector
wavefront distortions → beam quality
wavefronts
waveguide modes → modes
wavelength
wavelength beam combining → spectral beam combining
wavenumber
waveplates
wedge prisms
wire grid polarizers → polarizers
working distance
zero dispersion wavelength
Optical materials
 absorbing coatings → black coatings
absorbing coatings → black coatingsactive fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
active laser media → gain media
amplifier fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
amplifying fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers black coatings ceramic gain media chromium-doped gain media clustering composite laser crystals
concentration of dopant → doping concentration
crown glasses → optical glasses
diffusion bonding → composite laser crystals
domain engineering → periodic poling
domain inversion → periodic poling
domain-patterned semiconductors → orientation-patterned semiconductors
doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers doped insulator lasers doping concentration
electric-field poling → periodic poling
erbium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers erbium-doped gain media
ferroelectric domain engineering → periodic poling
flint glasses → optical glasses fluoride fibers fluoride glasses
fluorozirconate fibers → fluoride fibers
forsterite crystals → chromium-doped gain media four-level and three-level gain media
fused silica fibers → silica fibers gain media
gray tracking → photodarkening
green-induced infrared absorption → photodarkening
ground state laser transitions → four-level and three-level gain media
heavy metal fluoride fibers → fluoride fibers
hybrid laser crystals → composite laser crystals index matching fluids infrared optics
lanthanide lasers → rare-earth-doped gain media laser crystals laser crystals versus glasses
laser fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
laser gain media → gain media
laser glasses → laser crystals versus glasses
laser media → gain media
left-handed metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
light-induced absorption → photodarkening
lithium niobate and tantalate → nonlinear crystal materials
manufacturing of optics → optical fabrication
metamaterials → photonic metamaterials mirror substrates
Nd:YAG → YAG lasers
Nd:YLF → YLF lasers
Nd:YVO4 → vanadate lasers
negative-index materials → photonic metamaterials
neodymium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers neodymium-doped gain media nonlinear crystal materials
number density of dopant → doping concentration
OP-GaAs → orientation-patterned semiconductors optical fabrication optical glasses orientation-patterned semiconductors
percentage of doping → doping concentration periodic poling
phonon-terminated lasers → vibronic lasers phosphate glasses phosphors
photo-induced attenuation → photodarkening
photochromic damage → photodarkening photochromic materials photodarkening
photoinduced losses → photodarkening photonic metamaterials
praseodymium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
quasi-three-level lasers → four-level and three-level gain media rare-earth-doped fibers rare-earth-doped gain media
reabsorption in gain media → four-level and three-level gain media
refractive index fluids → index matching fluids
self-darkening materials → photochromic materials silica fibers
super-black coatings → black coatings
three-level gain media → four-level and three-level gain media
thulium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers transition-metal-doped gain media
transparency intensity → four-level and three-level gain media tungstate lasers vanadate lasers vibronic lasers YAG lasers
Yb:YAG, Yb:KGW, Yb:KYW, Yb:glass, … → ytterbium-doped gain media YLF lasers
ytterbium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers ytterbium-doped gain media
Fiber optics and waveguides
 acceptance angle in fiber optics
acceptance angle in fiber opticsactive fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
active optical cables → fiber-optic links adiabatic soliton compression
air-guiding fibers → hollow-core fibers
amplifier fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
amplifying fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
angle cleaving → cleaving of fibers
aperiodic fiber gratings → fiber Bragg gratings bandwidth–distance product
bat ear controllers → fiber polarization controllers
beat length → polarization beat length bend losses
birefringent fibers → polarization-maintaining fibers
bound modes → guided waves
Bragg fibers → photonic bandgap fibers
Bragg grating sensors → fiber-optic sensors Brillouin scattering
bulk lasers versus fiber lasers → fiber lasers versus bulk lasers
bundled fibers → fiber bundles
C band → optical fiber communications
chalcogenide fibers → mid-infrared fibers
chemical vapor deposition → fiber fabrication
cladding → fiber cladding cladding mode strippers cladding modes
cladding-pumped fibers → double-clad fibers
cleavers → fiber cleavers cleaving of fibers
connectors for fibers → fiber connectors
core → fiber core core-less end caps
coupled-mode theory → mode coupling
crystalline fibers → single-crystal fibers cut-off wavelength
depressed cladding → fiber cladding
depressed cladding → fibers differential mode delay dispersion-decreasing fibers
dispersion-flattened fibers → dispersion-shifted fibers dispersion-shifted fibers distributed amplifiers distributed Bragg reflector lasers
distributed sensors → fiber-optic sensors
doped fiber amplifiers → fiber amplifiers
doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers double-clad fibers
effective modal bandwidth → modal bandwidth effective mode area effective refractive index
effective step-index profile → step-index fibers
effectively single-mode fibers → single-mode fibers
elliptical core → polarization-maintaining fibers
endlessly single-mode fibers → photonic crystal fibers erbium-doped fiber amplifiers
erbium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
fabrication of optical fibers → fiber fabrication
femtosecond fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers few-mode fibers fiber amplifiers fiber Bragg gratings fiber bundles fiber cables fiber cladding fiber cleavers fiber collimators fiber connectors fiber core fiber-coupled diode lasers fiber couplers
fiber coupling stages → fiber launch systems
fiber drawing towers → fiber fabrication
fiber end caps → core-less end caps fiber fabrication fiber fuse fiber joints fiber lasers fiber lasers versus bulk lasers fiber launch systems fiber loop mirrors
fiber manufacturing → fiber fabrication
fiber modes → fibers
fiber-optic cables → fiber cables
fiber-optic communications → optical fiber communications
fiber-optic connectors → fiber connectors fiber-optic links fiber-optic networks
fiber-optic patch cords → fiber cables fiber-optic plates fiber-optic pump combiners fiber-optic sensors fiber-optic tapers fiber optics fiber patch cables fiber polarization controllers
fiber preforms → fiber fabrication
fiber rods → fiber bundles
fiber sensors → fiber-optic sensors fiber simulation software
fiber splices → fiber joints fiber to the home fibers
figure-of-eight laser → mode-locked fiber lasers fluoride fibers
fluorozirconate fibers → fluoride fibers
free-space modes → modes
fused silica fibers → silica fibers fusion splicing of fibers Giles parameters
glass fibers → fibers graded-index fibers group velocity dispersion
guided modes → modes guided waves
heavy metal fluoride fibers → fluoride fibers high-power fiber lasers and amplifiers higher-order modes higher-order solitons
holey fibers → photonic crystal fibers hollow-core fibers
index-depressed cladding → fiber cladding
infrared fibers → mid-infrared fibers
inner cladding → double-clad fibers insertion loss intermodal dispersion
L band → optical fiber communications large-core fibers large mode area fibers
laser fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
lateral modes → higher-order modes
launching light into fibers → fiber launch systems leaky modes
long-period fiber Bragg gratings → fiber Bragg gratings LP modes
Marcuse formula → mode radius master oscillator fiber amplifier mechanical fiber splices microbends of fibers
microstructure fibers → photonic crystal fibers mid-infrared fibers
misalignment of fibers → fiber joints modal bandwidth
modal dispersion → intermodal dispersion
modal refractive index → effective refractive index
mode area → effective mode area mode coupling
mode cut-off → cut-off wavelength mode field converters
mode field diameter → mode radius mode-locked fiber lasers mode radius
mode solvers → fiber simulation software
mode strippers → cladding mode strippers modes
modified chemical vapor deposition → fiber fabrication
monocrystalline fibers → single-crystal fibers
monomode fibers → single-mode fibers multi-core fibers
multi-mode fibers → multimode fibers multimode fibers
multimode pump combiners → fiber-optic pump combiners
multimode waveguides → waveguides nanofibers
neodymium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
nonlinear fiber loop mirrors → fiber loop mirrors nonlinear polarization rotation nonlinear pulse distortion nonlinearities
normalized frequency → V number numerical aperture
optical fiber cables → fiber cables optical fiber communications
optical fiber sensors → fiber-optic sensors
optical fiber technology → fiber optics
optical fibers → fibers
optical frequency domain reflectometry → fiber-optic sensors
optical nanofibers → nanofibers
optical networks → fiber-optic networks optical power monitors
optical sensors → fiber-optic sensors optical strain sensors optical temperature sensors optical time-domain reflectometers
PANDA fibers → polarization-maintaining fibers
parabolic index fibers → graded-index fibers
patch cables → fiber patch cables
phase constant → propagation constant phosphate glasses photonic bandgap fibers photonic crystal fibers
photonic power → power over fiber
photosensitivity → fiber Bragg gratings
pigtailed diode lasers → fiber-coupled diode lasers planar waveguides
plasma deposition methods → fiber fabrication plastic optical fibers polarization beat length
polarization controllers → fiber polarization controllers polarization-maintaining fibers polarization mode dispersion
polarization-preserving fibers → polarization-maintaining fibers
polycrystalline fibers → mid-infrared fibers
polymer optical fibers → plastic optical fibers
power monitors → optical power monitors power over fiber
praseodymium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
precision fiber cleavers → fiber cleavers
preforms → fiber fabrication propagation constant
pulse break-up → nonlinear pulse distortion quasi-soliton pulses
radiation modes → cladding modes Raman amplifiers
Raman effect → Raman scattering Raman scattering rare-earth-doped fibers
rod-in-tube method → fiber fabrication
S band → optical fiber communications
sampled grating lasers → distributed Bragg reflector lasers
sapphire fibers → single-crystal fibers self-phase modulation
semiconductor fiber lasers → fiber lasers
sensors → fiber-optic sensors silica fibers single-crystal fibers
single-mode cut-off → single-mode fibers single-mode fibers single-polarization fibers
solution doping → fiber fabrication specialty fibers
splicing → fusion splicing of fibers
spontaneous Raman scattering → Raman scattering step-index fibers
stimulated Brillouin scattering → Brillouin scattering
stimulated Raman scattering → Raman scattering
strain sensors → optical strain sensors
stress rods → polarization-maintaining fibers
stretched-pulse fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers tapered fibers telecom fibers
telecom windows → optical fiber communications
temperature sensors → optical temperature sensors
thulium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers
tolerances for fiber coupling → fiber joints
transmission loss → insertion loss
transverse modes → higher-order modes
tunneling modes → leaky modes
ultrafast fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers V number
vapor deposition methods → fiber fabrication
wave breaking → nonlinear pulse distortion waveguide dispersion waveguide lasers
waveguide modes → modes waveguides
ytterbium-doped fibers → rare-earth-doped fibers zero dispersion wavelength
Optical resonators
 alignment sensitivity of optical resonators
alignment sensitivity of optical resonatorsaxial mode spacing → free spectral range cavities
cavity design → resonator design crystalline mirrors distributed feedback lasers
doubly resonant cavities → resonant frequency doubling
dynamically unstable resonators → unstable resonators enhancement cavities etalons Fabry–Perot interferometers finesse
free-space modes → modes free spectral range Fresnel number Gires–Tournois interferometers
green problem → intracavity frequency doubling
guided modes → modes Hermite–Gaussian modes
high-Q resonators → Q factor higher-order modes intracavity frequency doubling
laser cavities → laser resonators
laser resonator design → resonator design laser resonators
lateral modes → higher-order modes
left-handed metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
microcavities → cavities
misalignment → alignment sensitivity of optical resonators mode cleaner cavities mode competition mode hopping mode matching modes
monocrystalline mirrors → crystalline mirrors
negative-index materials → photonic metamaterials nonplanar ring oscillators
optical cavities → cavities optical frequency photonic metamaterials Q factor
quality factor → Q factor reference cavities resonant frequency doubling
resonant second-harmonic generation → resonant frequency doubling resonator design
resonator mode spacing → free spectral range ring lasers ring resonators
semiconductor mirrors → crystalline mirrors
sensitivity to alignment → alignment sensitivity of optical resonators
singly resonant cavities → resonant frequency doubling stability zones of optical resonators
transverse modes → higher-order modes
unidirectional ring lasers → ring lasers unstable resonators
waveguide modes → modes
Nonlinear optics
 acceptance angle in nonlinear optics → critical phase matching
acceptance angle in nonlinear optics → critical phase matchingangle phase matching → critical phase matching
artificial saturable absorbers → saturable absorbers
attosecond pulses → high harmonic generation B integral birefringent phase matching
birefringent walk-off → spatial walk-off Brillouin scattering coherence length critical phase matching cross-phase modulation crystal ovens
difference frequency generation → sum and difference frequency generation
domain engineering → periodic poling
domain inversion → periodic poling
domain-patterned semiconductors → orientation-patterned semiconductors
doubly resonant cavities → resonant frequency doubling
doubly resonant oscillators → optical parametric oscillators effective mode area effective nonlinear coefficient
electric-field poling → periodic poling electro-optic effect electro-optic modulators
fast absorbers → saturable absorbers
ferroelectric domain engineering → periodic poling
fiber-feedback parametric oscillators → optical parametric oscillators fiber loop mirrors
fiber-optic parametric amplifiers → optical parametric amplifiers four-wave mixing
fourth-harmonic generation → frequency quadrupling
frequency conversion → nonlinear frequency conversion frequency doubling frequency quadrupling frequency tripling
green problem → intracavity frequency doubling group velocity mismatch high harmonic generation hyper Raman scattering
idler wave → parametric amplification intracavity frequency doubling Kerr effect Kerr lens
Kerr nonlinearity → Kerr effect
lithium niobate and tantalate → nonlinear crystal materials mid-infrared laser sources
mode area → effective mode area noncritical phase matching
nonlinear amplification → parametric amplification
nonlinear coefficient → effective nonlinear coefficient nonlinear crystal materials
nonlinear fiber loop mirrors → fiber loop mirrors nonlinear frequency conversion nonlinear index nonlinear optics nonlinear polarization nonlinear polarization rotation nonlinear pulse distortion
nonlinear refractive index → nonlinear index
nonlinear self-focusing → self-focusing nonlinearities
OP-GaAs → orientation-patterned semiconductors optical parametric amplifiers optical parametric generators optical parametric oscillators optical rectification orientation-patterned semiconductors parabolic pulses parametric amplification
parametric amplifiers → optical parametric amplifiers parametric fluorescence
parametric generators → optical parametric generators
parametric oscillators → optical parametric oscillators periodic poling phase matching phase-matching bandwidth
phase mismatch → phase matching
phase-sensitive amplification → parametric amplification
Poynting vector walk-off → spatial walk-off
pulse break-up → nonlinear pulse distortion pump depletion
pump threshold → threshold pump power quasi-phase matching quasi-soliton pulses Raman amplifiers
Raman effect → Raman scattering
Raman fiber lasers → Raman lasers Raman gain Raman lasers Raman scattering
Raman self-frequency shift → solitons
red–green–blue sources → RGB sources resonant frequency doubling
resonant second-harmonic generation → resonant frequency doubling RGB sources saturable absorbers
saturation parameter → saturable absorbers
second-harmonic generation → frequency doubling self-focusing self-phase modulation
self-similar pulse propagation → parabolic pulses
self-steepening → Kerr effect
similaritons → parabolic pulses
singly resonant cavities → resonant frequency doubling
singly resonant oscillators → optical parametric oscillators
slow absorbers → saturable absorbers
soliton fission → supercontinuum generation soliton period
soliton self-frequency shift → solitons solitons spatial walk-off
spontaneous Raman scattering → Raman scattering
stimulated Brillouin scattering → Brillouin scattering
stimulated Raman scattering → Raman scattering Stokes shift sum and difference frequency generation supercontinuum generation
sync-pumped parametric oscillators → optical parametric oscillators
t-waves → terahertz radiation
tandem OPOs → optical parametric oscillators
temperature phase matching → noncritical phase matching
temperature-stabilized ovens → crystal ovens temporal walk-off terahertz radiation
third-harmonic generation → frequency tripling threshold pump power
type I or type II phase matching → phase matching visible lasers
walk-off angle → spatial walk-off
walk-off compensation → spatial walk-off
wave breaking → nonlinear pulse distortion z-scan measurements
Photonic devices
 achromatic lenses → lenses
acousto-optic deflectors
acousto-optic frequency shifters
acousto-optic modulators
acousto-optic Q switches
acousto-optic tunable filters
achromatic lenses → lenses
acousto-optic deflectors
acousto-optic frequency shifters
acousto-optic modulators
acousto-optic Q switches
acousto-optic tunable filtersaluminum mirrors → metal-coated mirrors anti-reflection coatings
aperiodic fiber gratings → fiber Bragg gratings arrayed waveguide gratings
artificial saturable absorbers → saturable absorbers
attenuators → optical attenuators autocorrelators avalanche photodiodes Babinet–Soleil compensators balanced photodetection
bat ear controllers → fiber polarization controllers
beam blocks → beam dumps
beam diagnostics → beam profilers beam dumps beam profilers beam shapers beam shutters
beam traps → beam dumps
beam viewing cards → laser viewing cards Berek compensators
Berek tunable waveplates → Babinet–Soleil compensators
birefringent filters → birefringent tuners birefringent tuners
Bragg grating sensors → fiber-optic sensors Bragg mirrors Brewster plates brightness converters
broadband light sources → superluminescent sources
bulk Bragg gratings → volume Bragg gratings
calorimeters → optical energy meters
camera sensors → image sensors cameras
cavity dumpers → pulse pickers
CCD sensors → image sensors chirped mirrors
choppers → optical choppers
circular multipass cells → multipass gas cells
cleaner cavities → mode cleaners
CMOS sensors → image sensors
coatings → dielectric coatings
cold cathode fluorescent lamps → fluorescent lamps cold mirrors
color filters → optical filters common-path interferometers
compact fluorescent lamps → fluorescent lamps crystalline mirrors
delay lines → optical delay lines
detector cards → laser viewing cards dichroic mirrors dielectric coatings dielectric mirrors
differential photodetection → balanced photodetection
diode drivers → laser diode drivers
diode modules → laser diode modules dispersion-compensation modules
dispersive delay lines → optical delay lines dispersive mirrors
distributed mirrors → Bragg mirrors
distributed sensors → fiber-optic sensors
doped fiber amplifiers → fiber amplifiers
double-chirped mirrors → chirped mirrors
doubly resonant oscillators → optical parametric oscillators
dual-segment photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors electro-optic modulators electroabsorption modulators
electron beam evaporation → dielectric mirrors
energy meters → optical energy meters enhancement cavities erbium-doped fiber amplifiers etalons Faraday isolators Faraday rotators
fast absorbers → saturable absorbers fiber amplifiers fiber Bragg gratings fiber couplers
fiber-feedback parametric oscillators → optical parametric oscillators fiber loop mirrors
fiber-optic parametric amplifiers → optical parametric amplifiers fiber-optic sensors fiber polarization controllers
fiber sensors → fiber-optic sensors
filters → optical filters Fizeau interferometers fluorescent lamps
Franz–Keldysh effect → electroabsorption modulators
gas absorption cells → multipass gas cells
gas discharge lamps → fluorescent lamps
Geiger mode photodiodes → avalanche photodiodes Gires–Tournois interferometers
gold mirrors → metal-coated mirrors
gradient-index filters → rugate filters
half-wave plates → waveplates
half-wave voltage → Pockels cells halogen lamps
harmonic separators → dichroic mirrors
heat control filters → cold mirrors
Herriott multipass cells → multipass gas cells
holographic bulk gratings → volume Bragg gratings hot mirrors
image converters → image intensifiers and image converters image intensifiers and image converters image sensors incandescent lamps infrared cameras
infrared detector cards → laser viewing cards infrared detectors infrared emitters
infrared sensor cards → laser viewing cards infrared viewers integrated optics
integrated optoelectronic devices → photonic integrated circuits integrating spheres intensity modulators
intensity modulators → optical modulators
intensity profile measurement → beam profilers
interference coatings → dielectric coatings interferometers
ion beam sputtering → dielectric mirrors
joule meters → optical energy meters
knife edge beam profilers → beam profilers
laser beam shapers → beam shapers
laser beam shutters → beam shutters laser diode drivers laser diode modules
laser energy meters → optical energy meters
laser line mirrors → laser mirrors laser mirrors
laser power meters → optical power meters
laser pump chambers → pump chambers laser viewing cards
lateral effect photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
LEDs → light-emitting diodes lenses
light choppers → optical choppers light-emitting diodes liquid crystal displays liquid crystal modulators
long-pass gas cells → multipass gas cells
long-period fiber Bragg gratings → fiber Bragg gratings
long-wave infrared detectors → infrared detectors
luxmeters → photometers Lyot filters
Mach–Zehnder interferometers → interferometers
matrix method for multilayer structures → dielectric mirrors metal–semiconductor–metal photodetectors metal-coated mirrors Michelson interferometers
microchannel plate detectors → photomultipliers mid-infrared laser sources mode cleaner cavities mode cleaners mode field converters
modulators → optical modulators
monocrystalline mirrors → crystalline mirrors
multilayer coatings → dielectric coatings
multilayer mirrors → dielectric mirrors multipass gas cells neutral density filters noise eaters
nonlinear fiber loop mirrors → fiber loop mirrors
objectives for photography → photographic objectives optical attenuators optical choppers optical clocks optical clockworks
optical coatings → dielectric coatings optical delay lines optical energy meters
optical fiber sensors → fiber-optic sensors optical filters
optical frequency domain reflectometry → fiber-optic sensors
optical interference coatings → dielectric coatings
optical isolators → Faraday isolators optical modulators optical parametric amplifiers optical parametric generators optical parametric oscillators optical power meters optical power monitors
optical sensors → fiber-optic sensors optical strain sensors optical temperature sensors opto-isolators
optocouplers → opto-isolators optoelectronics
optronics → optoelectronics output couplers p–i–n photodiodes
parametric amplifiers → optical parametric amplifiers
parametric generators → optical parametric generators
parametric oscillators → optical parametric oscillators
Pfund cells → multipass gas cells phase modulators photo cameras photocathodes photoconductive switches
photocouplers → opto-isolators
photodetector arrays → photodiode arrays photodetectors photodiode arrays photodiodes
photoelectric detectors → photoemissive detectors photoemissive detectors photographic objectives photometers photomultipliers photon counting
photon science → photonics photonic integrated circuits photonics
photoreceivers → photodetectors
photosensitivity → fiber Bragg gratings phototransistors phototubes
planar lightwave circuits → photonic integrated circuits planar waveguides Pockels cell drivers Pockels cells
polarization controllers → fiber polarization controllers
polarization rotators → Faraday rotators position-sensitive detectors
power meters → optical power meters
power monitors → optical power monitors pulse pickers pulse shapers pump chambers pyroelectric detectors Q switches
quadrant photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors quantum dots quantum photonics quantum wells quarter-wave mirrors
quarter-wave plates → waveplates
rotating disc choppers → optical choppers
rotating slit profilers → beam profilers rugate filters
saturable absorber mirrors → semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors saturable absorbers saturable Bragg reflectors
saturation parameter → saturable absorbers
scanning beam profilers → beam profilers
scanning delay lines → optical delay lines
semiconductor mirrors → crystalline mirrors semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors
sensor cards → laser viewing cards
sensors → fiber-optic sensors Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensors silicon photonics
silver mirrors → metal-coated mirrors
singly resonant oscillators → optical parametric oscillators
slow absorbers → saturable absorbers
spatial filters → mode cleaners
strain sensors → optical strain sensors superluminescent diodes superluminescent sources supermirrors
surface-emitting LEDs → light-emitting diodes
sync-pumped parametric oscillators → optical parametric oscillators
tandem OPOs → optical parametric oscillators tapered amplifiers
temperature sensors → optical temperature sensors terahertz detectors terahertz sources thermal detectors
thermal power meters → optical power meters
thin-film coatings → dielectric coatings
thin-film mirrors → dielectric mirrors
traveling-wave photodetectors → velocity-matched photodetectors
tunable light sources → wavelength-tunable light sources tunable optical filters
tunable retarders → Babinet–Soleil compensators
tuning fork choppers → optical choppers
two-mirror beam shapers → beam shapers Twyman–Green interferometers
Ulbricht spheres → integrating spheres
ultrafast pulse shapers → pulse shapers
V coatings → anti-reflection coatings
vacuum tube photodetectors → phototubes variable optical attenuators
variable waveplates → Babinet–Soleil compensators velocity-matched photodetectors volume Bragg gratings
wavelength meters → wavemeters wavelength-tunable light sources wavemeters waveplates
White cells → multipass gas cells white light interferometers white light sources
Light detection and characterization
 autocorrelators
avalanche photodiodes
balanced photodetection
bandwidth
autocorrelators
avalanche photodiodes
balanced photodetection
bandwidthbeam diagnostics → beam profilers beam profilers
beam viewing cards → laser viewing cards
calorimeters → optical energy meters cameras
coherent detection → optical heterodyne detection
delayed self-heterodyne interferometer → self-heterodyne linewidth measurement detectivity
detector cards → laser viewing cards
differential photodetection → balanced photodetection
dispersive spectral analysis → spectrometers
dual-segment photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
effective pulse duration → pulse duration
electric field reconstruction → pulse characterization
emission spectrum → optical spectrum
energy meters → optical energy meters
energy of laser pulses → pulse energy focal plane arrays
Fourier transform spectral phase interferometry → spectral phase interferometry Fourier transform spectroscopy
frequency domain interferometry → spectral phase interferometry frequency-resolved optical gating
Geiger mode photodiodes → avalanche photodiodes
heterodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection
homodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection illuminance
image converters → image intensifiers and image converters image intensifiers and image converters infrared cameras
infrared detector cards → laser viewing cards infrared detectors
infrared sensor cards → laser viewing cards
infrared spectroscopy → spectroscopy
infrared thermography → thermal imaging infrared viewers
intensity → optical intensity
intensity profile measurement → beam profilers irradiance
joule meters → optical energy meters
knife edge beam profilers → beam profilers
laser energy meters → optical energy meters
laser power meters → optical power meters laser viewing cards
lateral effect photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
light intensity → optical intensity
long-wave infrared detectors → infrared detectors luminous efficacy and efficiency luminous flux
luxmeters → photometers
microchannel plate detectors → photomultipliers microchannel plates monochromators
monochromators → spectrometers night vision devices noise-equivalent power
optical bandwidth → bandwidth optical energy meters optical heterodyne detection optical intensity optical power optical power meters optical power monitors optical spectrum optical spectrum analyzers
optical wavelength → wavelength photo cameras
photoacoustic spectroscopy → spectroscopy photocathodes photoconductive detectors
photodetector arrays → photodiode arrays photodetectors photodiode arrays photodiodes
photoelectric detectors → photoemissive detectors photoelectric effect
photoemission → photoelectric effect photoemissive detectors photometers photometry photomultipliers photon counting
photoreceivers → photodetectors
photoresistors → photoconductive detectors phototransistors phototubes position-sensitive detectors
power meters → optical power meters
power monitors → optical power monitors pulse characterization pulse duration pulse energy
pulse length → pulse duration
pulse width → pulse duration pyroelectric detectors
quadrant photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors quantum efficiency
quantum yield → quantum efficiency radiance radiant energy radiant flux
radiant sensitivity → responsivity
radiometers → radiometry radiometry responsivity
rotating slit profilers → beam profilers
scanning beam profilers → beam profilers
scanning spectrometers → spectrometers self-heterodyne linewidth measurement sensitivity
sensor cards → laser viewing cards Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensors solar-blind photodetectors
specific detectivity → detectivity spectral brightness spectral phase spectral phase interferometry
spectral radiance → radiance spectral response of a photodetector
spectral width → bandwidth spectrographs spectrometers
spectrometry → spectroscopy
spectroradiometers → spectrometers spectroscopy
spectrum → optical spectrum terahertz detectors thermal detectors thermal imaging
thermal power meters → optical power meters
time domain spectroscopy → Fourier transform spectroscopy
vacuum tube photodetectors → phototubes
vacuum wavelength → wavelength
visible-blind detectors → solar-blind photodetectors wavelength
wavelength meters → wavemeters wavemeters wavenumber
Optoelectronics
 avalanche photodiodes
broad area laser diodes
avalanche photodiodes
broad area laser diodescamera sensors → image sensors
CCD sensors → image sensors
CMOS sensors → image sensors
diode arrays → diode bars diode bars diode lasers diode stacks distributed Bragg reflector lasers distributed feedback lasers
dual-segment photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors electro-optics electroabsorption modulators external-cavity diode lasers
fast axis → diode bars
Franz–Keldysh effect → electroabsorption modulators
Geiger mode photodiodes → avalanche photodiodes
image converters → image intensifiers and image converters image intensifiers and image converters image sensors
integrated optoelectronic devices → photonic integrated circuits
intersubband transitions → quantum cascade lasers
laser diode bars → diode bars
laser diode stacks → diode stacks laser diodes
lateral effect photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
LEDs → light-emitting diodes light-emitting diodes
microchannel plate detectors → photomultipliers microchannel plates optoelectronics
optronics → optoelectronics photocathodes photoconductive detectors photoconductive sampling photoconductive switches
photodetector arrays → photodiode arrays photodetectors photodiode arrays photodiodes photomultipliers photon counting photonic integrated circuits
photoreceivers → photodetectors
photoresistors → photoconductive detectors phototransistors phototubes
planar lightwave circuits → photonic integrated circuits position-sensitive detectors
quadrant photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors quantum cascade lasers
sampled grating lasers → distributed Bragg reflector lasers
semiconductor diode lasers → diode lasers semiconductor lasers silicon photonics
single-emitter laser diodes → broad area laser diodes
slow axis → diode bars
stack lasers → diode stacks superluminescent diodes
surface-emitting LEDs → light-emitting diodes surface-emitting semiconductor lasers
vacuum tube photodetectors → phototubes
Lasers
 absorption cross sections → transition cross sections
absorption cross sections → transition cross sectionsabsorption efficiency → pump absorption
absorption saturation → pump absorption
active laser media → gain media
active mirror → thin-disk lasers active mode locking
active stabilization of lasers → stabilization of lasers alexandrite lasers alignment lasers alignment sensitivity of optical resonators
alkali vapor lasers → gas lasers all-solid-state lasers
allowed transitions → forbidden transitions
alpha factor → linewidth enhancement factor
amplification bandwidth → gain bandwidth amplified spontaneous emission
amplifier transitions → laser transitions
amplitude noise → intensity noise
applications of lasers → laser applications
arc lamp pumping → lamp-pumped lasers
argon fluoride lasers → excimer lasers argon ion lasers
athermal lasers → radiation-balanced lasers beam collimators beam combining beam pointing fluctuations
beam pointing stability → beam pointing fluctuations blue lasers brightness converters broad-area laser diodes bulk lasers
bulk lasers versus fiber lasers → fiber lasers versus bulk lasers
carbon dioxide lasers → CO2 lasers
cascade lasing → cooperative lasing cavity dumping ceramic gain media
characterization of laser beams → laser beam characterization
chemical lasers → gas lasers
chillers → laser cooling units
chillers for lasers → laser cooling units chromium-doped gain media
class-A and class-B regime of a laser → relaxation oscillations CO2 lasers coherent beam combining composite laser crystals
concentration of dopant → doping concentration continuous-wave operation
cooling units for lasers → laser cooling units cooperative lasing
copper vapor lasers → gas lasers core-less end caps
cross lasers → alignment lasers
cross sections → transition cross sections cryogenic lasers
damage threshold → laser-induced damage depolarization loss
diffusion bonding → composite laser crystals
diode arrays → diode bars diode bars
diode drivers → laser diode drivers diode lasers
diode modules → laser diode modules diode-pumped lasers diode stacks direct diode lasers
disk lasers → thin-disk lasers dispersion management distributed Bragg reflector lasers distributed feedback lasers doped insulator lasers
doped insulator lasers → solid-state lasers doping concentration
duty cycle → quasi-continuous-wave operation dye lasers edge-emitting semiconductor lasers
effective cross sections → effective transition cross sections effective transition cross sections
efficiency of a laser → wall-plug efficiency
electrical-to-optical efficiency → wall-plug efficiency
emission cross sections → transition cross sections
emission linewidth → linewidth end pumping
entropy balance of lasers → radiation-balanced lasers erbium-doped gain media excimer lasers excited-state absorption external-cavity diode lasers
extinction ratio → polarization of light eye-safe lasers
fast axis → diode bars
femtosecond fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers femtosecond lasers fiber-coupled diode lasers
fiber end caps → core-less end caps fiber lasers fiber lasers versus bulk lasers
figure-of-eight laser → mode-locked fiber lasers
flash lamp pumping → lamp-pumped lasers
fluorine lasers → excimer lasers
FM mode locking → mode locking forbidden transitions
forsterite crystals → chromium-doped gain media four-level and three-level gain media
Frantz–Nodvick equation → gain saturation free electron lasers gain gain bandwidth gain clamping
gain compression → gain saturation gain efficiency gain media
gain modules → laser heads gain narrowing gain saturation gain switching gas lasers green lasers
green problem → intracavity frequency doubling
ground state laser transitions → four-level and three-level gain media
heat capacity lasers → quasi-continuous-wave operation
helium–cadmium lasers → gas lasers helium–neon lasers
Henry factor → linewidth enhancement factor high brightness laser diodes high-power fiber lasers and amplifiers high-power lasers
hybrid laser crystals → composite laser crystals
hybrid mode locking → mode locking
in-band pumping → optical pumping
in-plane lasers → edge-emitting semiconductor lasers
induced focusing → thermal lensing injection locking injection seeding intensity noise
intensity-to-phase coupling → linewidth enhancement factor interlocks
intersubband transitions → quantum cascade lasers intracavity frequency doubling intracavity laser absorption spectroscopy
ion lasers → argon ion lasers
krypton fluoride lasers → excimer lasers
krypton ion lasers → argon ion lasers lamp-pumped lasers laser applications laser beam characterization
laser beam combining → beam combining laser beams
laser cavities → laser resonators laser cooling units
laser cross sections → transition cross sections laser crystals laser crystals versus glasses laser design laser development
laser diode bars → diode bars laser diode collimators laser diode drivers laser diode modules
laser diode stacks → diode stacks laser diodes
laser disks → thin-disk lasers
laser dyes → dye lasers laser dynamics
laser gain → gain
laser gain media → gain media
laser glasses → laser crystals versus glasses
laser hazards → laser safety laser heads laser-induced damage laser light
laser line mirrors → laser mirrors laser lines
laser linewidth → linewidth
laser media → gain media laser mirrors laser modeling
laser modules → laser heads laser noise laser optics
laser oscillators → lasers laser physics laser pointers
laser pump chambers → pump chambers
laser radiation → laser light laser resonators
laser rods → rod lasers laser safety laser specifications laser threshold laser transitions lasers lasing without inversion
lifetime broadening → gain bandwidth
line lasers → alignment lasers
linear polarization → polarization of light linewidth linewidth enhancement factor
longitudinal pumping → end pumping lower-state lifetime master laser master oscillator fiber amplifier master oscillator power amplifier medical lasers microchip lasers mid-infrared laser sources
misalignment → alignment sensitivity of optical resonators mode competition mode hopping mode-locked diode lasers mode-locked fiber lasers mode-locked lasers
mode lockers → mode locking devices mode locking mode locking devices
modeling → laser modeling modes of laser operation molecular lasers
monochromaticity → linewidth
monofrequency lasers → single-frequency lasers monolithic solid state lasers nanosecond lasers narrow-linewidth lasers
Nd:YAG → YAG lasers
Nd:YLF → YLF lasers
Nd:YVO4 → vanadate lasers neodymium-doped gain media
nitrogen lasers → gas lasers
noise → laser noise
noise reduction → stabilization of lasers
nonlinear mirror mode locking → mode locking nonplanar ring oscillators
number density of dopant → doping concentration
one-atom lasers → single-atom lasers
operation modes of lasers → modes of laser operation
optical damage → laser-induced damage
optical damage threshold → laser-induced damage
optical gain → gain optical pumping
optically pumped semiconductor lasers → vertical external-cavity surface-emitting lasers
optics for lasers → laser optics
orange lasers → yellow and orange lasers oscillators output couplers output coupling efficiency parasitic lasing passive mode locking
percentage of doping → doping concentration
phase synchronization of lasers → synchronization of lasers
phonon-terminated lasers → vibronic lasers picosecond lasers
pigtailed diode lasers → fiber-coupled diode lasers
pointing stability → beam pointing fluctuations
polarization extinction ratio → polarization of light polarization of light
power amplifiers → master oscillator power amplifier
power efficiency → wall-plug efficiency power scaling of lasers pump absorption pump chambers pump depletion pump parameter
pump threshold → threshold pump power Q-switched lasers quantum cascade lasers quasi-continuous-wave operation
quasi-three-level lasers → four-level and three-level gain media
radiance scaling of lasers → power scaling of lasers radiation-balanced lasers
Raman fiber lasers → Raman lasers Raman lasers
rational harmonic mode locking → active mode locking
reabsorption in gain media → four-level and three-level gain media
red–green–blue sources → RGB sources red lasers
regenerative mode locking → active mode locking relative intensity noise relaxation oscillations RGB sources ring lasers rod lasers ruby lasers
safety → laser safety
sampled grating lasers → distributed Bragg reflector lasers
saturation of absorption → pump absorption
saturation of gain → gain saturation
scalability → power scaling of lasers
scaling procedures → power scaling of lasers Schawlow–Townes linewidth seed lasers
self-injection locking → injection locking self-starting mode locking self-terminating laser transitions
semiconductor diode lasers → diode lasers
semiconductor disk lasers → vertical external-cavity surface-emitting lasers
semiconductor fiber lasers → fiber lasers semiconductor lasers
sensitivity to alignment → alignment sensitivity of optical resonators
SESAM mode-locked lasers → mode-locked lasers side pumping single-atom lasers
single-emitter laser diodes → broad area laser diodes single-frequency lasers single-frequency operation single-mode operation
single transverse mode operation → single-mode operation
single-wavelength lasers → single-frequency lasers slab lasers slave laser slope efficiency
slow axis → diode bars solid state lasers soliton mode locking spatial hole burning
specifications for lasers → laser specifications spectral beam combining
spectral linewidth → linewidth spiking
spontaneous emission factor → Schawlow–Townes linewidth
spot lasers → alignment lasers stabilization of lasers
stack lasers → diode stacks stimulated emission
stimulated emission cross sections → transition cross sections
stretched-pulse fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers surface-emitting semiconductor lasers
surgical lasers → medical lasers synchronization of lasers tapered laser diodes
thermal depolarization → depolarization loss thermal lensing thin-disk lasers
three-level gain media → four-level and three-level gain media threshold pump power thresholdless lasers
timing synchronization → synchronization of lasers titanium–sapphire lasers transition cross sections transition-metal-doped gain media
transitions → laser transitions
transparency intensity → four-level and three-level gain media tunable lasers tungstate lasers twisted-mode technique
ultrafast diode lasers → mode-locked diode lasers
ultrafast fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers ultrafast laser physics ultrafast lasers
ultrashort pulse generation → ultrafast lasers ultraviolet lasers
unidirectional ring lasers → ring lasers upconversion lasers
uses of lasers → laser applications vanadate lasers VCSEL arrays vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers vertical external-cavity surface-emitting lasers vibronic lasers
violet lasers → blue lasers visible lasers wall-plug efficiency waveguide lasers
wavelength beam combining → spectral beam combining wavelength-swept lasers
wavelength-tunable lasers → tunable lasers wavelength tuning
weakly allowed transitions → forbidden transitions X-ray lasers
xenon bromide lasers → excimer lasers YAG lasers
Yb:YAG, Yb:KGW, Yb:KYW, Yb:glass, … → ytterbium-doped gain media yellow and orange lasers YLF lasers ytterbium-doped gain media
Optical amplifiers
 active laser media → gain media
active laser media → gain mediaamplification bandwidth → gain bandwidth amplification factor amplified spontaneous emission amplifier chains amplifier noise
amplifier stages → amplifier chains
amplifier transitions → laser transitions
amplifiers → optical amplifiers
doped fiber amplifiers → fiber amplifiers
dual-stage amplifiers → amplifier chains erbium-doped fiber amplifiers
excess noise → amplifier noise
femtosecond pulse amplifiers → ultrafast amplifiers fiber amplifiers fiber simulation software
Frantz–Nodvick equation → gain saturation gain gain bandwidth gain clamping
gain compression → gain saturation gain efficiency gain equalization
gain flattening → gain equalization gain guiding gain media gain narrowing gain saturation Giles parameters high-power fiber lasers and amplifiers
laser amplifiers → optical amplifiers
laser gain → gain
laser gain media → gain media
laser media → gain media laser transitions
lifetime broadening → gain bandwidth master oscillator fiber amplifier master oscillator power amplifier
mode solvers → fiber simulation software
multi-stage amplifiers → amplifier chains multipass amplifiers noise figure nonlinear pulse distortion optical amplifiers
optical gain → gain parasitic lasing
picosecond pulse amplifiers → ultrafast amplifiers
power amplification factor → amplification factor
power amplifiers → master oscillator power amplifier
pulse break-up → nonlinear pulse distortion Raman amplifiers rate equation modeling regenerative amplifiers
saturation of gain → gain saturation seed lasers semiconductor optical amplifiers slave laser small-signal gain stimulated emission tapered amplifiers transition-metal-doped gain media
transitions → laser transitions ultrafast amplifiers
wave breaking → nonlinear pulse distortion
Vision, displays and imaging
 aberrations → optical aberrations
afocal optical systems
aperture stops
astigmatism
aberrations → optical aberrations
afocal optical systems
aperture stops
astigmatismbeam diagnostics → beam profilers beam profilers
beam viewing cards → laser viewing cards
camera sensors → image sensors cameras
CCD sensors → image sensors
circle of confusion → imaging with a lens
CMOS sensors → image sensors
coma → optical aberrations condensers
confocal microscopy → confocal scanning microscopes confocal scanning microscopes conjugate planes deformable mirrors
demagnification → magnification depth of field depth of focus
detector cards → laser viewing cards diaphragms
dual-segment photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors entrance and exit pupil
exit pupil → entrance and exit pupil
eyepieces → ocular lenses f-number
f-stop number → f-number
field curvature → optical aberrations field lenses field of view field stops fluorescence microscopy
hand lenses → magnifying glasses holography hyperfocal distance hyperspectral imaging
image converters → image intensifiers and image converters
image distortion → optical aberrations image intensifiers and image converters image planes image sensors
image space → object and image space imaging imaging with a lens infrared cameras
infrared detector cards → laser viewing cards
infrared sensor cards → laser viewing cards
infrared thermography → thermal imaging infrared viewers
intensity profile measurement → beam profilers
intermediate image planes → image planes
knife edge beam profilers → beam profilers laser microscopy
laser radar → LIDAR laser viewing cards
lateral effect photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
lens speed → f-number LIDAR
light detection and ranging → LIDAR liquid crystal displays loupes magnification magnifying glasses microscope objectives microscopes
multiphoton microscopy → fluorescence microscopy multispectral imaging
nanoscopy → laser microscopy object and image space
objective lenses → objectives objectives
objectives for photography → photographic objectives ocular lenses optical aberrations optical coherence tomography
optical images → imaging
optical imaging → imaging optical profilometers
optical spaces → object and image space
optical surface profilers → optical profilometers phosphors photo cameras photographic objectives position-sensitive detectors principal points and principal planes
profilometers → optical profilometers
pupils → entrance and exit pupil
quadrant photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
red–green–blue sources → RGB sources RGB sources
rotating slit profilers → beam profilers
scanning beam profilers → beam profilers
sensor cards → laser viewing cards spectral imaging spherical aberrations
stimulated emission depletion microscopy → fluorescence microscopy
surface profilers → optical profilometers telecentric lenses telescopes thermal imaging
two-photon microscopy → fluorescence microscopy vignetting
Lightwave communications
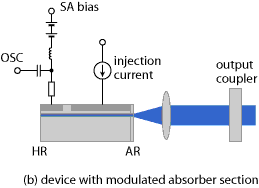 active optical cables → fiber-optic links
active optical cables → fiber-optic linksadd–drop multiplexers → wavelength division multiplexing amplifier noise bandwidth–distance product bit error rate
C band → optical fiber communications
data transmission → optical data transmission differential mode delay dispersion compensation dispersion compensation modules
dispersion-flattened fibers → dispersion-shifted fibers dispersion management dispersion-shifted fibers distributed amplifiers
doped fiber amplifiers → fiber amplifiers
effective modal bandwidth → modal bandwidth electronic dispersion compensation erbium-doped fiber amplifiers
excess noise → amplifier noise few-mode fibers fiber amplifiers
fiber-optic communications → optical fiber communications fiber-optic links fiber-optic networks fiber to the home
free-space communications → free-space optical communications free-space optical communications graded-index fibers
GRISMs → dispersion compensation
integrated optoelectronic devices → photonic integrated circuits
intensity modulators → optical modulators
inter-satellite communications → free space optical communications
L band → optical fiber communications
laser communications → free-space optical communications
laser links → free space optical communications
laser transmitters → free space optical communications
lightwave communications → optical data transmission modal bandwidth mode division multiplexing mode-locked diode lasers
modulators → optical modulators multi-core fibers
optical communications → optical data transmission optical data transmission optical fiber communications optical modulators
optical networks → fiber-optic networks
optical telegraph → free space optical communications optical time-domain reflectometers
parabolic index fibers → graded-index fibers photonic integrated circuits
planar lightwave circuits → photonic integrated circuits polarization mode dispersion Raman amplifiers
S band → optical fiber communications
satellite communications → free space optical communications
SDM fibers → space division multiplexing semiconductor optical amplifiers
space communications → free space optical communications space division multiplexing telecom fibers
telecom windows → optical fiber communications
telecommunications → optical data transmission time division multiplexing
transversal filters → electronic dispersion compensation
ultrafast diode lasers → mode-locked diode lasers wavelength division multiplexing
Quantum optics
 amplified spontaneous emission
amplitude-squeezed light
amplified spontaneous emission
amplitude-squeezed lightanti-Stokes fluorescence cooling → optical refrigeration
antibunching → nonclassical light
black body radiation → thermal radiation
coherent detection → optical heterodyne detection coherent states Doppler cooling Doppler limit
dressed states → Sisyphus cooling
entangled states → photons
fluorescent cooling → optical refrigeration
Fock states → nonclassical light
Glauber states → coherent states
heterodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection
homodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection
in-band pumping → optical pumping
incandescence → thermal radiation
key distribution → quantum cryptography laser cooling
laser refrigeration → optical refrigeration lasing without inversion light forces
no-cloning theorem → quantum cryptography nonclassical light
one-atom lasers → single-atom lasers
optical bomb → superradiance optical heterodyne detection optical molasses optical pumping optical refrigeration
optical traps → light forces parametric fluorescence
phase-squeezed light → squeezed states of light photon counting
photon number states → nonclassical light
photon statistics → nonclassical light photons
polarization gradient cooling → Sisyphus cooling
quadrature squeezing → squeezed states of light quantum cryptography quantum dots quantum key distribution quantum noise quantum optics quantum photonics quantum wells
Rabi frequency → Rabi oscillations Rabi oscillations radiation pressure recoil limit Schawlow–Townes linewidth shot noise single-atom lasers Sisyphus cooling spontaneous emission
spontaneous emission factor → Schawlow–Townes linewidth squeezed states of light standard quantum limit superfluorescence superradiance thermal radiation thresholdless lasers vacuum noise
Zeeman slowing → Doppler cooling
Fluctuations and noise
 active stabilization of lasers → stabilization of lasers
amplified spontaneous emission
active stabilization of lasers → stabilization of lasers
amplified spontaneous emissionamplitude noise → intensity noise
antibunching → nonclassical light balanced photodetection
coherent detection → optical heterodyne detection coherent states
cycle jitter → timing jitter
delayed self-heterodyne interferometer → self-heterodyne linewidth measurement detectivity
differential photodetection → balanced photodetection
emission linewidth → linewidth
Fock states → nonclassical light frequency noise
Glauber states → coherent states Gordon–Haus jitter
heterodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection
homodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection injection locking injection seeding intensity noise
jitter → timing jitter
laser linewidth → linewidth laser noise linewidth
monochromaticity → linewidth narrow-linewidth lasers
noise → laser noise noise eaters noise-equivalent power noise figure
noise reduction → stabilization of lasers noise specifications nonclassical light optical heterodyne detection phase noise
phase-squeezed light → squeezed states of light
phase synchronization of lasers → synchronization of lasers
photon number states → nonclassical light
photon statistics → nonclassical light power spectral density
pulse-to-pulse jitter → timing jitter Q-switching instabilities
quadrature squeezing → squeezed states of light quantum noise
r.m.s. values → power spectral density recirculating fiber loops relative intensity noise
residual jitter → timing jitter Schawlow–Townes linewidth self-heterodyne linewidth measurement
self-injection locking → injection locking sensitivity shot noise signal-to-noise ratio
specific detectivity → detectivity
specifications of noise and fluctuations → noise specifications
spectral linewidth → linewidth
spectral power density → power spectral density spontaneous emission
spontaneous emission factor → Schawlow–Townes linewidth squeezed states of light stabilization of lasers standard quantum limit synchronization of lasers timing jitter
timing noise → timing jitter timing phase
timing synchronization → synchronization of lasers vacuum noise
Wiener–Khinchin theorem → power spectral density
Optical metrology
 absolute phase → carrier–envelope offset
absolute phase → carrier–envelope offsetabsorption spectroscopy → laser absorption spectroscopy
attosecond pulse spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy autocorrelators avalanche photodiodes
beam diagnostics → beam profilers beam profilers
beam propagation factor → M2 factor
beam quality factor → M2 factor beat note carrier–envelope offset
characterization of laser beams → laser beam characterization
coherent detection → optical heterodyne detection
coherent time-resolved spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy
confocal microscopy → confocal scanning microscopes confocal scanning microscopes
cycle jitter → timing jitter
damage threshold → laser-induced damage decibel
delayed self-heterodyne interferometer → self-heterodyne linewidth measurement
dispersive spectral analysis → spectrometers distance measurements with lasers
dual-segment photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
effective pulse duration → pulse duration
electric field reconstruction → pulse characterization
energy of laser pulses → pulse energy Fizeau interferometers fluorescence spectroscopy
fly-wheel oscillators → frequency metrology
Fourier transform spectral phase interferometry → spectral phase interferometry Fourier transform spectroscopy
frequency chains → frequency metrology
frequency domain interferometry → spectral phase interferometry frequency metrology frequency-resolved optical gating
frequency standards → optical frequency standards
Geiger mode photodiodes → avalanche photodiodes
heterodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection
homodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection illuminance
infrared spectroscopy → spectroscopy
infrared thermography → thermal imaging integrating spheres
intensity profile measurement → beam profilers interferometers irradiance
jitter → timing jitter
knife edge beam profilers → beam profilers laser absorption spectroscopy laser beam characterization
laser distance meters → distance measurements with lasers laser-induced damage
laser radar → LIDAR laser rangefinders laser spectroscopy
lateral effect photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors LIDAR
light detection and ranging → LIDAR
luxmeters → photometers M2 factor
Mach–Zehnder interferometers → interferometers
metrology → optical metrology Michelson interferometers
microchannel plate detectors → photomultipliers microscope objectives microscopes monochromators
monochromators → spectrometers optical clocks optical clockworks optical coherence tomography
optical damage → laser-induced damage
optical damage threshold → laser-induced damage optical flats optical frequency
optical frequency metrology → frequency metrology optical frequency standards optical heterodyne detection
optical lattice clocks → optical frequency standards optical metrology optical power monitors optical profilometers optical spectrum analyzers
optical surface profilers → optical profilometers optical time-domain reflectometers phase shift method for distance measurements
photoacoustic spectroscopy → spectroscopy
photodetector arrays → photodiode arrays photodiode arrays photodiodes photometers
photometry → optical metrology photomultipliers phototransistors phototubes position-sensitive detectors power density
power monitors → optical power monitors power spectral density
profilometers → optical profilometers pulse characterization pulse duration pulse energy
pulse length → pulse duration pulse repetition rate
pulse-to-pulse jitter → timing jitter
pulse width → pulse duration pump–probe measurements
pump–probe spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy
quadrant photodiodes → position-sensitive detectors
quantum beat spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy
r.m.s. values → power spectral density radiance radiant energy radiant flux
radiometry → optical metrology
Raman spectroscopy → laser spectroscopy
range finding → distance measurements with lasers reference cavities
references surfaces → optical flats
remote ranging → distance measurements with lasers
repetition rate → pulse repetition rate
residual jitter → timing jitter
rotating slit profilers → beam profilers
scanning beam profilers → beam profilers
scanning spectrometers → spectrometers self-heterodyne linewidth measurement
self-phase-stabilized pulses → carrier–envelope offset signal-to-noise ratio spectral brightness spectral phase spectral phase interferometry
spectral power density → power spectral density
spectral radiance → radiance spectrographs spectrometers
spectrometry → spectroscopy spectrophotometers
spectroradiometers → spectrometers spectroscopy
surface profilers → optical profilometers thermal imaging
time domain spectroscopy → Fourier transform spectroscopy time-of-flight measurements time-resolved spectroscopy timing jitter
timing noise → timing jitter timing phase
transient absorption spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy triangulation Twyman–Green interferometers
Ulbricht spheres → integrating spheres
ultrafast spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy
vacuum tube photodetectors → phototubes
wavelength meters → wavemeters wavemeters white light interferometers
Wiener–Khinchin theorem → power spectral density z-scan measurements
Light pulses
 absolute phase → carrier–envelope offset
active mode locking
absolute phase → carrier–envelope offset
active mode lockingactive Q switching → Q switching additive-pulse mode locking adiabatic soliton compression
artificial saturable absorbers → saturable absorbers
attosecond pulses → high harmonic generation autocorrelators bandwidth-limited pulses carrier–envelope offset
cavity dumpers → pulse pickers cavity dumping chirp chirped mirrors chirped-pulse amplification
chirped pulses → chirp chromatic dispersion
comb spectra → frequency combs
damage threshold → laser-induced damage
dechirping → pulse compression differential mode delay dispersion compensation dispersion compensation modules dispersion-decreasing fibers
dispersion-flattened fibers → dispersion-shifted fibers dispersion management dispersion-shifted fibers
dispersive pulse compression → pulse compression
dispersive pulse stretchers → pulse stretchers dispersive wave divided-pulse amplification
double-chirped mirrors → chirped mirrors double pulses
duty cycle → quasi-continuous-wave operation
effective modal bandwidth → modal bandwidth
effective pulse duration → pulse duration
electric field reconstruction → pulse characterization
energy of laser pulses → pulse energy
f–2f interferometer → frequency combs
fast absorbers → saturable absorbers
femtosecond fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers femtosecond lasers
femtosecond pulse amplifiers → ultrafast amplifiers
few-cycle pulses → ultrashort pulses
figure-of-eight laser → mode-locked fiber lasers
FM mode locking → mode locking
Fourier limit → transform limit
Fourier transform spectral phase interferometry → spectral phase interferometry frequency combs
frequency domain interferometry → spectral phase interferometry frequency-resolved optical gating
frequency synthesizers → frequency combs fundamental mode locking gain switching Gaussian pulses
giant pulses → Q switching Gires–Tournois interferometers Gordon–Haus jitter
grating compressors → pulse compression
GRISMs → dispersion compensation group delay group delay dispersion group velocity group velocity dispersion group velocity mismatch harmonic mode locking Haus Master equation
heat capacity lasers → quasi-continuous-wave operation high harmonic generation higher-order solitons
hybrid mode locking → mode locking injection locking injection seeding instantaneous frequency Kelly sidebands Kerr lens mode locking Kuizenga–Siegman theory laser-induced damage
laser pulses → pulses
light pulses → pulses
master equation → Haus master equation modal bandwidth mode-locked diode lasers mode-locked fiber lasers mode-locked lasers
mode lockers → mode locking devices mode locking mode locking devices
multiple pulses → double pulses nanosecond lasers
nonlinear mirror mode locking → mode locking nonlinear polarization rotation
nonlinear pulse compression → pulse compression nonlinear pulse distortion
numerical modeling → pulse propagation modeling
optical damage → laser-induced damage
optical damage threshold → laser-induced damage
optical frequency synthesizers → frequency combs optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
optical pulse generation → pulse generation
optical pulses → pulses
optical rulers → frequency combs parabolic pulses passive mode locking
passive Q switching → Q switching peak power
phase synchronization of lasers → synchronization of lasers picosecond lasers
picosecond pulse amplifiers → ultrafast amplifiers prism pairs
pulse break-up → nonlinear pulse distortion pulse characterization pulse compression pulse duration pulse energy pulse front tilt pulse generation
pulse length → pulse duration pulse pickers pulse propagation modeling pulse repetition rate
pulse shape → Gaussian pulses pulse shapers pulse stretchers
pulse width → pulse duration pulsed laser deposition pulsed lasers pulses Q-switched lasers Q-switched mode locking Q switching Q-switching instabilities
QML threshold → Q-switched mode locking quasi-continuous-wave operation quasi-soliton pulses
Raman self-frequency shift → solitons
rational harmonic mode locking → active mode locking regenerative amplifiers
regenerative mode locking → active mode locking
repetition rate → pulse repetition rate
rubber band model → frequency combs
saturable absorber mirrors → semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors saturable absorbers saturable Bragg reflectors
saturation parameter → saturable absorbers sech2-shaped pulses
second-order dispersion → group delay dispersion
self-injection locking → injection locking
self-phase-stabilized pulses → carrier–envelope offset
self-referenced frequency combs → frequency combs
self-similar pulse propagation → parabolic pulses self-starting mode locking semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors
SESAM mode-locked lasers → mode-locked lasers
short pulses → pulses
similaritons → parabolic pulses
slow absorbers → saturable absorbers
soft aperture mode locking → Kerr lens mode locking
soliton compression → pulse compression soliton mode locking soliton period
soliton self-frequency shift → solitons solitons spectral phase spectral phase interferometry spectrograms
split-step Fourier technique → pulse propagation modeling
stretched-pulse fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers
supermodes → harmonic mode locking
symmetrized split-step Fourier method → pulse propagation modeling synchronization of lasers synchronous pumping
tilt of pulse fronts → pulse front tilt time–bandwidth product time-of-flight measurements
timing synchronization → synchronization of lasers transform limit ultrafast amplifiers
ultrafast diode lasers → mode-locked diode lasers
ultrafast fiber lasers → mode-locked fiber lasers ultrafast laser physics ultrafast lasers ultrafast optics
ultrafast pulse shapers → pulse shapers
ultrashort pulse generation → ultrafast lasers ultrashort pulses
unchirped pulses → chirp
wave breaking → nonlinear pulse distortion
Methods
 ABCD matrix
ABCD matrixabsorption spectroscopy → laser absorption spectroscopy active mode locking
active Q switching → Q switching
active stabilization of lasers → stabilization of lasers
add–drop multiplexers → wavelength division multiplexing
anti-Stokes fluorescence cooling → optical refrigeration
asynchronous sampling → optical sampling
atmospheric correction → laser guide stars
attosecond pulse spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy balanced photodetection beam combining
cavity design → resonator design chirped-pulse amplification
circle of confusion → imaging with a lens coherent beam combining
coherent detection → optical heterodyne detection
coherent time-resolved spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy
comb spectra → frequency combs
coupled-mode theory → mode coupling
dechirping → pulse compression
delayed self-heterodyne interferometer → self-heterodyne linewidth measurement
differential photodetection → balanced photodetection dispersion compensation dispersion management
dispersive pulse compression → pulse compression distance measurements with lasers divided-pulse amplification
domain engineering → periodic poling
domain inversion → periodic poling
domain-patterned semiconductors → orientation-patterned semiconductors Doppler cooling
doubly resonant cavities → resonant frequency doubling
dressed states → Sisyphus cooling
electric-field poling → periodic poling
electro-optic field mapping → electro-optic sampling electro-optic sampling end pumping eye protection
f–2f interferometer → frequency combs
ferroelectric domain engineering → periodic poling fiber simulation software fluorescence microscopy fluorescence spectroscopy
fluorescent cooling → optical refrigeration
FM mode locking → mode locking
Fourier transform spectral phase interferometry → spectral phase interferometry Fourier transform spectroscopy frequency combs
frequency domain interferometry → spectral phase interferometry frequency-resolved optical gating
frequency synthesizers → frequency combs
giant pulses → Q switching Giles parameters
goggles → eye protection
grating compressors → pulse compression
GRISMs → dispersion compensation
guide stars → laser guide stars harmonic mode locking Haus Master equation
heterodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection holography
homodyne detection → optical heterodyne detection
hybrid mode locking → mode locking imaging imaging with a lens
in-band pumping → optical pumping
infrared spectroscopy → spectroscopy
infrared thermography → thermal imaging injection locking injection seeding intracavity laser absorption spectroscopy Kerr lens mode locking
key distribution → quantum cryptography laser absorption spectroscopy
laser beam combining → beam combining laser cooling laser design laser development
laser distance meters → distance measurements with lasers
laser goggles → eye protection laser guide stars
laser hazards → laser safety laser marking laser microscopy laser modeling
laser radar → LIDAR
laser refrigeration → optical refrigeration
laser resonator design → resonator design laser safety laser specifications laser spectroscopy LIDAR
light detection and ranging → LIDAR light forces
longitudinal pumping → end pumping
manufacturing of optics → optical fabrication
master equation → Haus master equation mode coupling mode locking
mode solvers → fiber simulation software
modeling → laser modeling
multiphoton microscopy → fluorescence microscopy
nanoscopy → laser microscopy
no-cloning theorem → quantum cryptography
noise reduction → stabilization of lasers noncritical phase matching
nonlinear mirror mode locking → mode locking
nonlinear pulse compression → pulse compression
numerical modeling → pulse propagation modeling
OP-GaAs → orientation-patterned semiconductors optical coherence tomography optical fabrication
optical frequency synthesizers → frequency combs optical heterodyne detection
optical images → imaging
optical imaging → imaging optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
optical pulse generation → pulse generation optical pumping optical refrigeration
optical rulers → frequency combs optical sampling optical time-domain reflectometers
optical traps → light forces optical tweezers orientation-patterned semiconductors passive mode locking
passive Q switching → Q switching periodic poling phase matching
phase mismatch → phase matching phase shift method for distance measurements
phase synchronization of lasers → synchronization of lasers
photoacoustic spectroscopy → spectroscopy photoconductive sampling polarization beam combining
polarization coupling → polarization beam combining
polarization gradient cooling → Sisyphus cooling power scaling of lasers prism pairs pulse compression pulse generation pulse propagation modeling pump–probe measurements
pump–probe spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy Q-switched mode locking Q switching
QML threshold → Q-switched mode locking
quantum beat spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy quantum cryptography quantum key distribution quasi-phase matching
radiance scaling of lasers → power scaling of lasers Raman spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy → laser spectroscopy
range finding → distance measurements with lasers rate equation modeling
rational harmonic mode locking → active mode locking
ray transfer matrix → ABCD matrix reciprocity method recirculating fiber loops
regenerative mode locking → active mode locking
remote ranging → distance measurements with lasers resonant frequency doubling
resonant second-harmonic generation → resonant frequency doubling resonator design
rubber band model → frequency combs
safety → laser safety
safety glasses → eye protection
sampling → electro-optic sampling
scalability → power scaling of lasers
scaling procedures → power scaling of lasers self-heterodyne linewidth measurement
self-injection locking → injection locking
self-referenced frequency combs → frequency combs
sequential sampling → electro-optic sampling side pumping
singly resonant cavities → resonant frequency doubling Sisyphus cooling
sodium guide stars → laser guide stars
soft aperture mode locking → Kerr lens mode locking
soliton compression → pulse compression soliton mode locking
specifications for lasers → laser specifications spectral beam combining spectral phase interferometry
spectrometry → spectroscopy spectroscopy
split-step Fourier technique → pulse propagation modeling stabilization of lasers
stimulated emission depletion microscopy → fluorescence microscopy
supermodes → harmonic mode locking
symmetrized split-step Fourier method → pulse propagation modeling synchronization of lasers synchronous pumping
temperature phase matching → noncritical phase matching
terahertz spectroscopy → optical sampling thermal imaging time division multiplexing
time domain spectroscopy → Fourier transform spectroscopy time-of-flight measurements time-resolved spectroscopy
timing synchronization → synchronization of lasers
transient absorption spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy triangulation
tweezers → optical tweezers twisted-mode technique
two-photon microscopy → fluorescence microscopy
type I or type II phase matching → phase matching
ultrafast spectroscopy → time-resolved spectroscopy
wavelength beam combining → spectral beam combining wavelength division multiplexing wavelength tuning z-scan measurements
Zeeman slowing → Doppler cooling
Physical foundations
 absorption cross sections → transition cross sections
absorption cross sections → transition cross sectionsabsorption efficiency → pump absorption
absorption saturation → pump absorption
adjoint modes → resonator modes
allowed transitions → forbidden transitions
alpha factor → linewidth enhancement factor
amplifier transitions → laser transitions
axial modes → resonator modes
band gap
bandwidth
birefringent walk-off → spatial walk-off
black body radiation → thermal radiation
breakdown → laser-induced breakdown
carrier lifetime → upper-state lifetime
causality
cavity bandwidth → resonator modes
cavity modes → resonator modes
cavity resonances → resonator modes
chemiluminescence
concentration quenching → quenching
conical emission → laser-induced breakdown
cross relaxation → energy transfer
cross sections → transition cross sections
damage threshold → laser-induced damage
dark current
dispersion relations → Kramers–Kronig relations
Doppler broadening
effective cross sections → effective transition cross sections
effective transition cross sections
electro-optic effect
electro-optics
electroluminescence
emission cross sections → transition cross sections
emission linewidth → linewidth
emission spectrum → optical spectrum
energy migration → energy transfer
energy transfer
entangled states → photons
excited-state absorption
fast light → superluminal transmission
faster than light → superluminal transmission
fiber simulation software
fluorescence
fluorescence lifetime → upper-state lifetime
fluorescence quenching → quenching
forbidden transitions
Frantz–Nodvick equation → gain saturation
Füchtbauer–Ladenburg equation
gain compression → gain saturation
gain guiding
gain narrowing
gain saturation
Henry factor → linewidth enhancement factor
homogeneous broadening
homogeneous saturation
incandescence → thermal radiation
induced focusing → thermal lensing
inhomogeneous broadening
inhomogeneous saturation
intensity-to-phase coupling → linewidth enhancement factor
interference
inversion → population inversion
Kerr effect
Kerr lens
Kerr nonlinearity → Kerr effect
Kramers–Kronig relations
laser cross sections → transition cross sections
laser-induced breakdown
laser-induced damage
laser linewidth → linewidth
laser modeling
laser physics
laser transitions
left-handed metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
linewidth
linewidth enhancement factor
luminescence
luminescence quenching → quenching
McCumber theory
metamaterials → photonic metamaterials
metastable states
mode competition
mode solvers → fiber simulation software
modeling → laser modeling
monochromaticity → linewidth
multi-phonon transitions
multiphonon absorption
multiphoton absorption
multiphoton ionization → laser-induced breakdown
near field and far field
negative-index materials → photonic metamaterials
non-radiative transitions
nonlinear polarization
nonlinear polarization waves → polarization waves
numerical modeling → pulse propagation modeling
optical bandwidth → bandwidth
optical breakdown → laser-induced breakdown
optical damage → laser-induced damage
optical damage threshold → laser-induced damage
optical frequency
optical interference → interference
optical phase
optical spectrum
pair-induced quenching → quenching
parametric nonlinearities
phase → optical phase
phase velocity
phonons
phosphorescence
photocurrent
photoelectric effect
photoemission → photoelectric effect
photoluminescence
photonic metamaterials
photons
plane waves
Pockels effect
polarization waves
population inversion
Poynting vector walk-off → spatial walk-off
propagation losses
pulse propagation modeling
pump absorption
quantum defect
quantum efficiency
quantum yield → quantum efficiency
quenching
Rabi frequency → Rabi oscillations
Rabi oscillations
radiance
radiation pressure
radiative lifetime
radioluminescence → luminescence
Raman effect → Raman scattering
Raman gain
Raman scattering
rate equation modeling
reciprocity method
resonator bandwidth → resonator modes
resonator modes
saturated output power → saturation power
saturation energy
saturation fluence → saturation energy
saturation intensity → saturation power
saturation of absorption → pump absorption
saturation of gain → gain saturation
saturation power
self-steepening → Kerr effect
slow light → velocity of light
small-signal gain
spatial hole burning
spatial walk-off
spectral linewidth → linewidth
spectral radiance → radiance
spectral width → bandwidth
spectrum → optical spectrum
speed of light → velocity of light
split-step Fourier technique → pulse propagation modeling
spontaneous Raman scattering → Raman scattering
standing wave pattern → interference
stimulated emission
stimulated emission cross sections → transition cross sections
stimulated Raman scattering → Raman scattering
superluminal transmission
superluminescence
symmetrized split-step Fourier method → pulse propagation modeling
t-waves → terahertz radiation
TEM modes → resonator modes
terahertz radiation
thermal lensing
thermal radiation
third-order dispersion
transition cross sections
transitions → laser transitions
two-photon absorption
upconversion
upconversion quenching → quenching
upper-state lifetime
vacuum velocity of light → velocity of light
velocity of light
walk-off angle → spatial walk-off
walk-off compensation → spatial walk-off
weakly allowed transitions → forbidden transitions
zero-phonon transition → McCumber theory
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar