Jumat, 23 Mei 2025
Pure Virgin Golden Dome Network at Good Gate (moving and flying mountains) electronic circuit microcomputer controller key nice (future satellite intelligent network in country networking future complete), with schematic display algorithm hardware logic solutions , AMNIMARJESLOW Goverment Project and then Welcome R & D shooter Inteligent networking Revolution invest commands
1. Circuit Analyzer electron IC networking
===========================================
Basic Brain Loud Thinking
=========================
1. Block Diagram : A large and Complex schematic diagram is frequently " summarized " in an accompanying block diagram . A block diagram is useful because it gives you a quick general view of the overall system . where one is provided , you can use it to identify the circuit because the blocks names it .
2. schematic analysis : schematic analysis consists in separating the overall electronic network component picture into its parts, so as to determine their nature , function and relationship . it is a process like anatomy will tell you about the " organs " found in schematics " bodies ."
These " organs " are individual circuits. taken separately , you will find each is easy to understand and recognize .
3. Active and Passive elements : Circuit elements are either active or passive . Passive elements are those which do not require an external source of power in order to function . Active elements that use external power , which they introduce into the circuit to modify an existing signal or to generate a new one .
4. External Power : When in active elements is included in a circuit the external power is generally shown as entering and leaving in a vertical direction , perpendicular to the signal flow .
5. Circuit Identification : The majority of circuit consists of a small number of passive element build around an active element.
6. Circuit Analyzer : identification circuit and compare to confirm our identification
7. Circuit Locator : to check and drawing parts to circuit at good position and location .
circuit Analyzer coding picture
===============================
8. Visual Inspection and Comfirm Complaint to be check performance
its means for good operating conditions in signal value tracing .
9. Waveform analysis and parts substitutes automatic checks.
II . MICRO COMPUTER
___________________
A. Characteristics of the Microcomputer : type of micro computer is a cabinet containing electronic circuits which perform the functions of the personal computer constructed on printed circuit boards . in the world of technology , chips are called " micro computers ' . micro computers are the offspring of the development of LSI chips for use in electronic calculators.
The function and composition of a microcomputer :
1. Storage Program
2. Consecutive control
in other words , the basic function of a computer are the storage in its memory of the commands which go to make up the program and a command cycle where the commands are conseccutively fetched and executed . the materials that are processed bu this series of operations are data .
The term microcomputer is used to describe a digital processing system that includes a minimum of a microprocessor, program memory, data memory, and input-output (I/O). Some microcomputer systems include additional components such as timers, counters, analog-to-digital converters, and so on. Thus, a microcomputer system can be anything from a large computer having hard disks, optical disks, SSD drives, printers, and plotters to a single chip embedded controller.
we are going to consider only the type of microcomputers that consists of a single silicon chip. Such microcomputer systems are also called microcontrollers and they are used in many household goods such as microwave ovens, TV remote control units, cookers, hi-fi equipment, CD players, personal computers, fridges, games consoles, etc. There are a large variety of microcontrollers available in the market place, ranging from 8-bits to 32-bits or even 64-bits. In this book we shall be looking at the programming and system design using a member of the 32-bit STM32 family of microcontrollers, manufactured by the STMicroelectronics. As we shall be seeing in the next chapter, STM32 family is based on the highly popular ARM processor architecture. In this chapter we shall be looking at the features of the microcontroller systems and describe their basic building blocks.
As large-scale integration and then very-large-scale integration progressively increased the number of transistors that could be placed on one semiconductor chip, so the processing capacity of microcomputers using such single chips grew commensurately. During the 1980s microcomputers came to be used widely in other applications besides electronic game systems and other relatively simple computer-based recreations. Increasingly powerful microcomputers began to be used in personal computer systems and workstations, for instance. High-performance microcomputer systems began to be used widely in business, in engineering, in “smart” or intelligent machines employed in the factory and office, and in military electronics systems.
Computer network ; is a series of computers connected to each other, whether by cables or wirelessly, that allow for effective communication. These computing devices include laptops, desktops, mobile phones, and even the ever-expanding array of IoT devices, such as cameras, refrigerators, and printers.
The main purpose of a computer network is to share information through interconnected nodes that can transmit, receive and exchange data, voice and video traffic, over the internet.
How does a computer network operate?
For a computer network to operate, there need to be switches, routers, and access points.
Switches connect and help internally secure computers and other devices to networks in homes or offices using cables. Access points, on the other hand, are switches that connect devices to networks wirelessly or without the use of cables.
Routers connect networks to other networks and act as dispatchers. They analyze data to be sent across a network, choose the best routes, and send it on its way.
There are various types of computer networking options available in today’s world, but some of the most popular ones are:
A computer network
Especially in the digital world, you need something that lets you connect to people within or outside the organization to keep the business running. And, of course, the larger an organization, the more complex the network becomes.
So, what exactly is a computer network?
Here at Intelligent Technical Solutions (ITS), we believe that the more you understand your technology, the better business decisions you make.
What is a Computer Network?
How does a computer network operate?
What are the types of computer networks?
When should you implement a computer network?
After reading, you should have a clear knowledge of a computer network and start planning on building or improving your existing network.
What is a Computer Network?
computer networks with different users
A computer network (AKA a data network) is a series of computers connected to each other, whether by cables or wirelessly, that allow for effective communication. These computing devices include laptops, desktops, mobile phones, and even the ever-expanding array of IoT devices, such as cameras, refrigerators, and printers.
The main purpose of a computer network is to share information through interconnected nodes that can transmit, receive and exchange data, voice and video traffic, over the internet.
How does a computer network operate?
For a computer network to operate, there need to be switches, routers, and access points.
Switches connect and help internally secure computers and other devices to networks in homes or offices using cables. Access points, on the other hand, are switches that connect devices to networks wirelessly or without the use of cables.
Routers connect networks to other networks and act as dispatchers. They analyze data to be sent across a network, choose the best routes, and send it on its way. In essence, routers connect your home and business to the world and help protect information from outside security threats.
What are the types of computer networks?
There are various types of computer networking options available in today’s world, but some of the most popular ones are:
Types of Computer Networks
PAN (Personal Area Network)
LAN (Local Area Network)
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network)
Below is a brief analysis of each type:
1. PAN (Personal Area Network)
PAN (Personal Area Network) is a computer network that is primarily personal devices, such as cordless mics, keyboards, and Bluetooth systems equipped within an extremely limited area.
You can use PAN to establish communication among these personal devices for connecting to a digital network and the internet.
2. LAN (Local Area Network)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a group of less than 5000 interconnected computers and peripheral devices connected in a limited area such as a school, laboratory, home, or office building.
Connecting your computer and printer to your home or office is a type of LAN. Since it is a private network, no outside regulatory body can control it.
3. WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN (Wide Area Network) is another crucial computer network spread across a large geographical area, so businesses situated at longer distances can easily communicate.
A WAN network system could be a connection of LANs with other LANs using telephone lines and radio waves. This type of networking is mostly limited to an office or organization.
4. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
A Metropolitan Area Network or MAN consists of a computer network across a city, college campus, or a small region–and is definitely larger than a LAN. Depending upon the type of configuration, this type of network allows you to cover an area in a maximum 50 km range.
MAN provides excellent support for an extensive network, so it is recommended to serve an entire city.
Microcomputer control circuitry contents
----------------------------------------
1. Characteristics of the microcomputer
2. Merhods for Expressing Data
3. Basic Microcomputer Logic Circuits ( Data Processing and Sync Signal )
4. Mictocomputer composituon and operation ( command fetching and execution )
5. Memory ( Memory System Composition )
6. Input / output Interfaces
7. Microcomputer examples and Tesla
8. Assembler Language and Programming .
=============================================================================
I. characteristic of the microcomputer ( Electron IC )
______________________________________________________
1. To clearly understand the difference between LSI microcomputers and personal computer.
2. To study the history of the mictocomputer and understand its true value : " design flexibility " .
3. To understand the fundamentals of the microcomputer and study the basics of microcomputer composition and operation .
4. To look at familiar examples and compare microcomputer control with electronic circuit control in order to understand the characteristic of microcomputer control.
5. To study the basic types , characteristics, and applications of microcomputers.
The function and composition of a microcomputer :
(1) A computer has the following two functions which can be called its basic principles :
a. Storage a program
b. Consecutive control
c. main unit with pure power storage.
in other words , the basic functions of a command cycle where the commands are consecutively fetched and executed . the materials processed by this series of operation are data.
(2) In order to carry out these operations , computer needs the following basic hardware. the basic hardware is exactly the same for a microcomputer . A microcomputer
consists of a CPU , a memory , and I/ O Ports , these are all interconnected by a sigmal line called a bus , so microcomputer must be pure power energy to on main unit control .
(3) Wired logic and Programmed logic
a. The development of the microcomputer made possible the following two methods for obtaining circuit functions :
a.1. Wired logic ( hardware method )
a.2. Programmed Logic ( can be hardware coding or Software coding ) method .
the wired logic methods as like as combinatiional logic circuit ( disital descriptive statistic value added ) and sequentials logic circuit ( inferensial statistic logic value added ) , the digital circuit is And circuit , OR circuit , 10 logic circuit , inverters , flip flops , and other logic circuit. this exactly what conventional electronic circuits are . the programmed logic method uses the microcomputer to perform the logic functions performed by the conventional electronic circuits are .
b. Looking at microcomputers on the semiconductor LSI chip level , because LSI chip is simply an integration of the hardware circuits , all of the LSI chip must be custom designed specifically for each use . LSI chip actually contains a built in computer , it is Programmable and , therefore , has design flexibility .
b. The development of the microcomputer we need the control procedure for the fulfilment of this function is called a "flowchart" .
II. Methods For Expressing Data
________________________________
Subject study to objectives until Predictive take and give location address :
1. To study the basic fundamentals of control , which are the input , processing , and output of data.
2. To learn what a digital quantity is and understand its characteristics.
3. To learn that all data handled by the computer is expressed in a binary code . Also to understand the hexadecimal notation that is used for convenience and to learn how to use it.
4. to learn that there are seven types ( 007 data locator ) of data : 1.numerical data , 2.character data and 3. logic data , 4.symbolic data ,5.differential data ,6.Tesla data , 7. random data .
Microcomputer description processing ;
______________________________________
I. Binary Code and binary numbers ; in microcomputer control , the data is handled as a digiral quantity. The word " digital " includes the meaning of " binary " , and binary means that data is being expressed a combination of two conditions , 0 and 1. the amoubt of data that can be expressed by either one of those symbols is called one bit , which is the smallest possible unit of data.
the reasons why binary code is used are as follow ;
1. it resists influence from noise and fluctuation in the ambient environment .
2. The " 0 " and " 1 " of the binary code can easily be replaced with low voltage and high voltage electronic signals.
3. Numerical data can be expressed as binary number and simple electronic circuits can be used to perform various mathematical operations.
II. many input / output parts such as sensors and actuators use analog operation. if these devices are connected to a microcomputer , the signals must be covered by other devices called A/D converter and D/A converter .
III. on the other hand , with a microcomputer whose purpose is control , the data exchanged between the microcomputer and the electronic machine between controlled is in the form numerical data or logic data or symbolic data . the only person who knows what the data actually means is the hardware programmer and software programmer .
welcome to control explain : As humans , we detect and become aware of various information via our five senses.
our minds gather this information , process it , and then act on it . in the same way , the machines we use can be considered to fulfill these same functions by detection and input of the necessary information , or data , processing it according to their purpose, and then , based on that data , output the appropriate control commands. This series of operation is what we call " control " . control system insight to sensor and actuator ; sensor is a device that detects some physical quantity such as voltage , temperature , rpm , mechanical motion , light vector motion , etc ., and converts that quantity into an electronic signal.
Also an actuator is a device such as an electromagnetic valve or motor which , in accordance with a control signals , convert electric , hydraulic or pneumatic energy , into mechanical energy.
A microcomputer is a control component which receives digital data input , digitally processes the data , and outputs digital data . here digital , in addition to meaning noncontinuous , also includes the meaning of binary .
A " port " is a terminal for the exchange of data between the microcomputer and an external device .
finally , lets review methods for expressing data .
(1) inside the microcomputer , all data is expressed in a binary code.
(2) Long rows of binary number data can be expressed as hexadecimal number for more
efficient notation .
(3) The data used in microcomputer control is usually logic data where each bit has
its own independent meaning .
III. Basic Microcomputer Logic circuits
_______________________________________
study objectives ;
1. to study the AND , OR , and NOT functions of the basic logic circuits of which microcomputer are composed.
2. to understand the thinking behind circuits composed of various combinations on the basic logic circuits .
3. To understand the concepts of multiplexers and three state buffers , and to study the features of the bus system .
4. To study the various flip flop circuits and the circuits in which they are used , multiplexers , encoders and decoders , three state buffers , and to understand the thinking behind data processing circuits as like as counters ,registers, shift registers ,data processing , sync signals .
IV . Microcomputer Composition and operation
____________________________________________
study objectives :
1. To gain and understanding of the relationship between hardware and software in the functioning of a microcomputer .
2. To learn the main functions af the two primary command types : those which control data processing , and those which control the flow of a program .
3. To understand the design of a microcomputer and the functions of the various components in this design .
4. to learn about fetching and execution of commands.
computers and electronic machines , a like are nothing more than assemblies and network instalation of nonfunctional or functional estimate situation , in animate parts until some person operate these to perform a specific function , its different automatic electronic machine networking . in general , the device or unit itself is called " hardware " , while the assembly of commands which is used to control and operate the hardware is called " software " .
Both large main frame computers and microcomputers perform the following tasks .
(1) Program storage
(2) sequential control
(3) Main unit pure energy
(4) fuzzy logic sensoring and transducer A/D to D/A convert fuzzy logic
(5) Math Co Sync Processing and Control
(6) Automation Networking to predictictive maintenance ,preventive maintenance system networking electronic machines.
(7) I/O with differential and integral using good CHIPs.
these commands are synchronized to a set time clock differential , fetched and interpreted one by one , and executed to process data .
example a few of these commands :
1. input data from location X .
2. Output data location Y
3. Perform calculation Q on data from location of the information to be processed or where to move data , in the mathelectronic we call orde 3 in differential technical .
Differential equation ( timer electronic equation to use moving synchronization)
================================================================================
A differential equation is an equation involving an unknown function y = f (x) and one or more of its derivatives . A solution to a differential equation is a function y = f (x) that satisfies the differential equation when f and its derivatives are substituted into the equation . Differential equations have three basic types — ordinary (ODE), partial (PDE), or differential-algebra (DAE), the equations can be further described based on attributes such as order, linearity, and degree. a practical example of the use of differentials is for synchronization of drive techniques both on AC and DC motors or servo motors, steppers in robotic systems or we know electronic drives where if we use many Robotic electronic motor wheel drives and move uniformly then a smooth motion calculation is needed at each robotic drive elbow or its joints, we explain as follows: Differential is part of the transmission system that distributes power to the drive wheel motor joint elbows. This is important when the elbow joints turn. Main Function of Differential: Divide power to the left and right wheel elbows: When the robot's wheel elbow movement is straight, the left and right motor wheels rotate at the same time. There are four common types of differentials: open, locked, limited slip, and torque vector. So Differential can be defined as the rate of change of a function due to changes in the independent variable of the function. Because differential equations describe the derivatives of a function, they give us information about how the function changes. Our goal is to use this information to predict future values of the function; in this way, differential equations give us something like a crystal ball.
V . Memory
==========
welcome om study ojectivea :
1. A knowledge of the types of memory and how they function .
2. An understanding of how data is written into the memory and how it is read out
3. A look at the construction of a memory system utilizing IC memories ( RAM 2114 , PROM 2716 ) AVAILABLE ON the market .
I. Type of memories and how they function :
________________________________________
(1) the entering of data into the memory is called to write in , and the taking of data from the memory is called to read out .
The terms write-in and read-out referred to together are called access.
(2) There are RAM and ROM type memories , and the RAM type can be further classified into the static type and the dynamic type.
the static type is mainly used in simple microcomputer control system.
For the static type , one flip flop is used for storage of each bit of data.
Accordingly, it can be considered that a large number of flip flops are in the RAM.
(3) ROMs can be classified into the masked ROM and the PROM; Data in the masked ROM is fixed in the memory when produced by the semiconductor manufacturer and are thus utilized as a mass produced product .
The PROM is suited for small production because it can be used by the user to write in data freely . the theory involved in erasing and writing in PROM data is complex and will thus be omitted here . The following circuit is equivalent to the state of the PROM after write -in .
Q1GPOChgdBXm_KmpIyw556GhJaAeniXjl9ulJrr9YsQ6N_Hji8/s320/20250530_063908.jpg"/>
II . Write - in and Read- out
_____________________________
(1) Data for write -in is sent to the datain lines and the address is sent to the address lines when the write-in pulse is applied , data is written in at the corresponding address.
Here, the prevention of writing in data at an unwanted address is worthy of attention. As a general rule , the write-in pulse should only be applied after the address and data have been explicitly set , and with the write -in terminal in the nonactive state.
(2) For Read -out , the contents of the corresponding address appear in the read-out data lines when the address to be read out is applied to the address line. and the write-in pulse is not output ( it can be considered that the read-out pulse is output ) For ROMs in which data has already been written in , the operation is very simple ; the data of the applicable address appear at the read-out lines by merely providing the address.
in this instance, as with the RAM , The time before data appear after the address has been changed ( tAC access time ) and the time from one read-out to the the next read-out ( tcj cycle time ) becomes important .
(3) By looking at the static RAM2114 and the PROM2716 , which are typical of memories on the market , we will learn how to organize a memory system.
here , caution is necessary regarding the use of the control signal .
Thus, for applications in which the microcomputer is inside equipment for control, a program which contains control procedures which do not need to be rewritten is contained in the ROM , the data which is managed by the program is stored in the RAM
furthermore , aside from the program , it is common for the ROM to also store fixed data necessary for the program .
in addition to the RAM holding data which executes the program by processing data, it can also be used a temporary memory space or , in other words , a work area for calculations .
in this way , one bit of a static RAM is the same as one flip-flop. As you know , we have already studied the register, which , by bringing together n.. flip flops , stores n .. bits of data. since this register is also a kind of memory , it can be considered that there are a large numberof these inside the static RAM .
the amount of data in bits for , in groups of eight bytes which can be stored in the entire memory is referred to as memory capacity .
The number of bits read out from the memory or written into the memory at one time is referred to as the wordlength of the memory .
in short , the memory is like a set of shelves in which each word length is put a way as partitioned data . Thus , any word length can be taken out from a particular shelf
( read - out ) or put away onto a shelf ( write-in ).
for this purpose an addressis used to indicate which shelf is to be used .
An important point here is the ability to freely write in or read out any data address. because the address line from the CPU is expressed as a binary code, a decoder is necessary to choose any address in the memory.
This is called the address decoder . with this decoder , how many address lines from the CPU do you think are necessary to designate a memory address of n bytes ?
A 1024 byte ( referred to as 1 K ) memory , for examples , needs 10, and a 2 K byte memory needs 11 address line . This can be understood from the figure .
A decoder is used to choose the memory address right .
The decoder output corresponds to the memory address .
At this point we shall summarize how to write in and read out. Data is written into the address when the data is sent to the write - in data lines, the address is sent to the address lines , and the write in pulse ( H ) is applied . Data appears in the read-out is sent to the address line. and the write -in pulse is not sent (L) (the read-out pulse is considered to be sent) .
The figure is a timing diagram for actions during read-out and Write-in. in the diagram , the time interval tcv is the minimum required time between one read-out and the next, or one write-in and the next . This is called Cycle time .
The PROM ( abbreviation of programmable ROM ) , which is capable of being freely written into by the user, is a small production item for control circuits in production equipment.
A device called the ROM writer is needed to write data into the PROM . Data stored in the PROM can be erased .
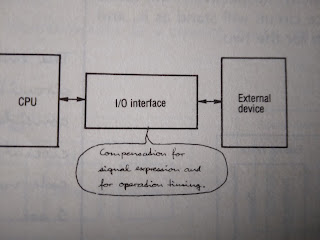
VI . INPUT / OUTPUT INTERFACES
------------------------------
LETS GO TO STUDY OBJECTIVES I/O INTEEFACES ;
1. THE BASIC FUNCTIONS OF INPUT / OUTPUT INTERFACES
2. THE FUNCTIONS and necessity of I/O ports
3. Input / output control methods and functions
VII . Microcomputer Examples ( viewit )
________________________________________
lets go and come on go outer space and big bang bang for study objectives ;
As a typical 8 - bit microcomputer , the intel i8085 will be used and an outline of its hardware and software will be studied .
VIII . Microcomputer Second Engine
___________________________________
Focus and system engine welcome again at :
1. The general characteristics of the 4 bit microcumputer will be studied .
2. An overall understanding will be gained concerning the hardware and software in
the MN 1400 4 bit microcomputer.
General Characteristics of the 4-bit microcomputer :
1. in the beginning project microcomputer have got at series texas instruments , at present almost all 4 - bit microcomputers are one chip . units being sold either resemble the TMS 1000 or are improved versions based on it . the TMS 1000 or are improved versions based on it.the TMS 1000 was first used in calculators , but afterward it tended more and more to be used in controls which have many uses .
1. The hardware characteristics for the 4 bit microcomputer are summarized as follows a. the program is in ROM and the data is in RAM , you know about smartphone , laptip , note book , PC computer , Digital TV and then all of them smart electronic machine as like as PABX , Sattelite node etc , its like to use that principle ROM and RAM teritory singularity .
b. The input port and the output Port are distinguished as separate .
The ouput port has been devisedin to such forms as series output , discrete output , and PLA output .
c. Unit types which have no interrupt function provide a sense input terminal , and program considerations are made , such as facilitation for easy flag inspection .
d. As well as containing a timer , it can include such things as an A/D converter and a PLL .
IX . Assembler Language and programming launching microchip and nanoelectronic implant
======================================================================================
lets go to R&D shooter electronic tactical ;
1. To attain an overall grasp of flowcharts and assembler language .
2. To open our eyes and brain at the technique of often-used program processing.
3. To understand the steps of system development .
4. To explain in the Future electronic implant , we use Neuralink good statue .
Analytic Geometri and Calculus for
setup Network Control circuitry rocket moving
Target Shooter schematic hardware Programmed
==============================================
Calculus and analytical geometry (timer, set up and recovery target shooter) direct comparative review on electronic warfare: 1. David Sling, 2. Arrow and 3. Iron Dome as the basis of the big project of captain america's shield, namely pure virgin golden dome.
Third orde calculus in electronic control
=========================================
"Third-order calculus" in the context of electronic control systems generally refers to the analysis and design of third-order dynamic systems, typically described by third-order differential equations. These systems arise in control engineering when modeling physical systems with three energy storage elements, such as inductors and capacitors in electrical systems or masses and springs in mechanical systems.
Here’s a breakdown of what this involves:
---
🔧 1. What Is a Third-Order System?
A third-order system has a third-order differential equation of the form:
a_3 \frac{d^3y(t)}{dt^3} + a_2 \frac{d^2y(t)}{dt^2} + a_1 \frac{dy(t)}{dt} + a_0 y(t) = b_0 u(t)
Where:
: output
: input (control signal)
: system parameters
This equation models the dynamics of the system.
In the Laplace domain, this becomes:
Y(s) = \frac{b_0}{a_3 s^3 + a_2 s^2 + a_1 s + a_0} U(s)
---
🧮 2. Analysis Techniques
a. Transfer Function
The system is typically analyzed via its transfer function:
G(s) = \frac{Y(s)}{U(s)} = \frac{b_0}{a_3 s^3 + a_2 s^2 + a_1 s + a_0}
b. Time-Domain Analysis
Step response
Impulse response
Stability: Use characteristic equation roots (poles).
Transient response: Overshoot, rise time, settling time.
c. Frequency-Domain Analysis
Bode plots
Nyquist plots
Gain/phase margins
🔄 3. Control System Design with Third-Order Systems
In control engineering, third-order systems may require:
a. Pole Placement
Assign desired poles using feedback control to meet design criteria.
b. PID or State-Space Control
PID can control third-order systems, but sometimes state-space or modern control techniques (e.g., pole assignment, LQR) are used.
c. Reduced-Order Approximations
Sometimes a third-order system is approximated as a second-order system if one pole is dominant.
⚡️ Example: Third-Order Electrical Circuit
Consider an RLC circuit with two capacitors and one inductor:
Governing equation:
L \frac{d^3i(t)}{dt^3} + R_1 \frac{d^2i(t)}{dt^2} + \frac{1}{C_1} \frac{di(t)}{dt} + \frac{1}{C_2} i(t) = V(t)
This is a third-order linear differential equation describing the system current.
🧠 Summary
Third-Order System Governed by 3rd-order differential equations
Transfer Function Has a cubic denominator (s³ term)
Analysis Time domain (response), frequency domain (stability)
Control Design PID, state-space, pole placement methods
Great! Let's walk through an example of an electronic component or circuit that results in a third-order differential equation, i.e., requires third-order calculus to analyze.
---
⚡️ Example: Third-Order RLC Circuit (Cascade of RLC Filters)
🔧 Circuit Description
Imagine a series RLC cascade made up of the following:
Stage 1: Resistor , Inductor
Stage 2: Resistor , Capacitor
Stage 3: Capacitor
This is a simplified model but leads to a third-order system.
🔄 Assumptions
Input voltage:
Output voltage: taken across
Goal: Find the transfer function
---
📘 Step 1: Derive the Governing Equation
You would write Kirchhoff's laws:
1. Use Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) around the loop.
2. Combine component relationships:
\text{Inductor: } V_L = L \frac{di}{dt}, \quad \text{Capacitor: } i_C = C \frac{dV}{dt}, \quad \text{Resistor: } V_R = Ri
This leads to an equation involving and and the currents/voltages across the components.
---
🧮 Step 2: Example Transfer Function (Standard Form)
For simplicity, let’s write the transfer function of a standard third-order RLC circuit in the form:
G(s) = \frac{K}{s^3 + a_2 s^2 + a_1 s + a_0}
Where:
is the gain (determined by resistors and input scaling),
are derived from the values of
You’d determine these from combining the differential equations obtained by analyzing each node or mesh in the circuit.
---
✅ Interpretation of Third-Order Behavior
A third-order RLC system will exhibit:
Up to three poles in the s-domain.
More complex transient behavior than second-order systems.
Potential for overshoot, oscillation, or instability, depending on pole placement.
May require state-space modeling or Laplace transforms to solve analytically.
---
📈 Applications
This type of third-order system shows up in:
Analog filter design (e.g., 3rd-order low-pass filters)
Power supply ripple filtering
Audio crossovers
RF circuits (filter stages)
Control circuits (like PID with added dynamics)
---
📌 Summary Table
Component Relationship Order Introduced
Resistor No order
Inductor +1 order
Capacitor +1 order
To get a third-order equation, combine three energy storage elements (e.g., 2 capacitors + 1 inductor).
---
Ah, got it — you're now looking for a third-order calculus example involving an active electronic component (like an op-amp, transistor, or amplifier), rather than just passive RLC elements.
Let’s go through a clear example involving an op-amp-based third-order active low-pass filter, which directly uses third-order calculus (i.e., third-order differential equations or third-order transfer functions) in its analysis.
---
⚡️ Example: Third-Order Active Low-Pass Filter Using Op-Amps
🔧 Circuit Overview
This circuit uses:
3 RC sections (each contributing a pole),
1 or more operational amplifiers (op-amps) to buffer and amplify,
Active design to avoid signal loss and allow better control.
---
🧱 Block Structure
A typical third-order active filter is implemented as a cascade of 3 first-order filter stages, like this:
Input → [RC + Op-Amp Stage 1] → [Stage 2] → [Stage 3] → Output
Each stage is a first-order low-pass filter, and cascading three of them gives you a third-order system.
---
🧮 Transfer Function
For a basic third-order low-pass filter:
G(s) = \frac{K}{(s/\omega_1 + 1)(s/\omega_2 + 1)(s/\omega_3 + 1)}
This expands to:
G(s) = \frac{K}{s^3 + a_2 s^2 + a_1 s + a_0}
Where:
: gain (set by resistor values in op-amp feedback paths),
: cutoff frequencies of each stage,
Coefficients come from multiplying the denominator terms.
---
🔍 Third-Order Calculus in Action
In the time domain, this corresponds to a third-order differential equation:
a_3 \frac{d^3y(t)}{dt^3} + a_2 \frac{d^2y(t)}{dt^2} + a_1 \frac{dy(t)}{dt} + a_0 y(t) = K \cdot u(t)
Where:
: input voltage,
: output voltage,
: determined by RC and op-amp configuration.
---
📘 Use Case Example: Audio Processing
In audio systems, third-order filters are used to cleanly attenuate high-frequency noise without overly distorting the signal.
Using op-amps ensures gain can be adjusted without signal degradation.
---
🧠 Summary
Feature Description
Active Component Op-amp
System Order Third-order (from 3 cascaded RC stages)
Calculus Involved Third-order differential equations
Time Domain Response involves 1st, 2nd, and 3rd derivatives of output
Frequency Domain Third-order transfer function with 3 poles
---
Great question! Let's now explore third-order calculus (i.e., third-order differential equations or their discrete-time equivalents) in the context of a digital circuit.
Since digital circuits work with discrete-time signals (not continuous-time like analog electronics), third-order behavior is modeled using difference equations rather than differential equations.
---
🧮 What Is “Third-Order Calculus” in Digital Circuits?
In digital signal processing (DSP) or digital control systems, a third-order system is described by a third-order difference equation — the discrete equivalent of a third-order differential equation.
---
🧾 1. Example: Third-Order Digital Filter (IIR)
🧠 Difference Equation
A third-order IIR (Infinite Impulse Response) filter may be described by:
y[n] = a_1 y[n-1] + a_2 y[n-2] + a_3 y[n-3] + b_0 x[n] + b_1 x[n-1] + b_2 x[n-2] + b_3 x[n-3]
Where:
: output signal
: input signal
: filter coefficients
The presence of makes it third-order
This is the discrete-time analogue of a third-order differential equation.
---
⚡️ 2. Digital Circuit Implementation
This filter can be implemented in hardware using:
Shift registers to store past values:
Multipliers for coefficients
Adders to sum terms
Clock for synchronization (discrete updates)
It's often implemented on:
FPGA, ASIC, or microcontroller
Or in software in a digital signal processor
---
🎛 3. Real-World Application
📦 Digital Control Systems
In embedded systems, you might design a third-order digital controller, like:
u[n] = k_1 e[n] + k_2 e[n-1] + k_3 e[n-2] + k_4 e[n-3]
: error signal (e.g., desired - measured)
This is essentially a third-order digital compensator
📡 Digital Filters
Third-order low-pass/high-pass filters for noise reduction in sensor data (IMU, audio, etc.)
Implemented on digital circuits to process real-time signals
---
🧠 Summary Table
Concept Analog Digital Equivalent
Third-order calculus 3rd derivative 3-step memory
Differential Equation
Solution Method Laplace transform Z-transform
Hardware Op-amps, RLC Flip-flops, adders, multipliers, FPGA/MCU
---
✅ Final Notes
"Third-order calculus" in digital systems means third-order difference equations, not derivatives.
Implemented via delays, feedback, and coefficients in a digital circuit.
---
Global positioning system ;
When discussing third-order calculus in the context of a GPS network, we're stepping into the field of navigation system modeling, dynamic estimation, and control theory — where higher-order derivatives like acceleration and jerk (the third derivative of position) become important.
---
🛰 What Does “Third-Order Calculus” Mean in GPS?
In GPS and navigation systems, third-order calculus typically refers to tracking and estimating:
Position (0th derivative)
Velocity (1st derivative of position)
Acceleration (2nd derivative)
Jerk (3rd derivative of position)
This is extremely useful in:
Kalman Filters for state estimation
GNSS/INS integration
Motion prediction in GPS-aided navigation
---
🧠 1. Third-Order Kinematic Model for GPS Tracking
A third-order system in a GPS network can be modeled as:
\begin{bmatrix}
\dot{x} \\
\dot{v} \\
\dot{a}
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
v \\
a \\
j
\end{bmatrix}
Where:
: position vector
: velocity vector
: acceleration vector
: jerk vector (assumed to be constant or modeled with noise)
This is called a third-order motion model and is used in state-space formulations.
---
📐 2. State-Space Representation for GPS Estimation
State Vector:
\mathbf{x} =
\begin{bmatrix}
x \\
v \\
a
\end{bmatrix}
Input (jerk):
\mathbf{u} = j
State Equation:
\mathbf{\dot{x}} = A\mathbf{x} + B\mathbf{u}
Where:
A = \begin{bmatrix}
0 & 1 & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1 \\
0 & 0 & 0
\end{bmatrix}, \quad
B = \begin{bmatrix}
0 \\
0 \\
1
\end{bmatrix}
---
📡 3. Application: Kalman Filter in GPS/INS
In GPS navigation systems (e.g., for autonomous vehicles or aircraft), a Kalman filter is often used to fuse:
GPS position data (slow, but globally accurate)
IMU data (fast, but prone to drift)
A third-order model helps smooth out GPS measurements by estimating jerk:
Reduces latency in estimating fast motion
Enables prediction between GPS signal updates
---
🔄 4. Example: Position Estimation with Jerk
Let’s say you’re tracking a moving car:
GPS updates every 1 second
But the car accelerates and decelerates sharply
Using a third-order filter, the system estimates:
Position
Velocity
Acceleration
Jerk
This improves prediction and reduces lag in motion estimation.
---
✅ Summary: Third-Order Calculus in GPS Networks
Concept Meaning
Third-order derivative Jerk (rate of change of acceleration)
Used for Precision motion modeling, Kalman filtering
Common in GNSS/INS fusion, high-accuracy tracking
Tools Kalman filters, state-space models, control systems
Why important? Improves prediction and smoothness in noisy GPS data
The Iron Dome is a real-time missile defense system developed by Israel to intercept short-range rockets and artillery. While much of its operation is classified, we can reasonably infer where third-order calculus concepts apply based on control systems, trajectory prediction, and guidance algorithms — all of which involve advanced modeling of motion and estimation.
Let’s explore what third-order calculus means in this high-tech context.
---
🛡️ What Is Third-Order Calculus in the Iron Dome?
In the context of the Iron Dome, "third-order calculus" usually refers to modeling the jerk — the third derivative of position — to predict and intercept high-speed projectiles.
Derivative Meaning
Position Where the missile is
Velocity How fast it’s moving
Acceleration How fast velocity is changing
Jerk How fast acceleration is changing
In such a dynamic and fast-response system, modeling jerk is critical for precise interception of fast-moving targets.
---
🎯 Where 3rd-Order Calculus Is Used in Iron Dome
1. Trajectory Prediction
The Iron Dome tracks enemy missiles and predicts their future position. It needs to model motion under rapidly changing acceleration — this requires third-order motion models:
\text{Target Position} = x(t),\quad v(t),\quad a(t),\quad \text{and possibly } j(t)
The intercept point is calculated using these high-order derivatives.
If only acceleration is considered, the system lags in fast maneuvers.
By modeling jerk, it can anticipate sudden changes in trajectory.
---
2. Kalman Filters with Higher-Order Models
The Iron Dome uses sensor fusion (radar + prediction models) and real-time Kalman filtering to estimate target states.
A third-order extended Kalman filter (EKF) estimates:
\mathbf{x} = [\text{position},\ \text{velocity},\ \text{acceleration}]
Improves filtering in non-linear and uncertain conditions (e.g., evasive maneuvers, wind).
---
3. Missile Guidance and Control
The Tamir interceptor missile is guided to the target using a proportional navigation law, enhanced with model predictive control (MPC) or other advanced guidance systems.
Real-time control systems may use state-space models including up to the third derivative for smoother path correction.
Helps ensure smooth guidance and avoids overshooting due to abrupt control changes.
---
🧮 Mathematical Model Example (Simplified)
State vector:
\mathbf{x}(t) = \begin{bmatrix} x(t) \\ v(t) \\ a(t) \end{bmatrix}
Dynamic model:
\frac{d\mathbf{x}}{dt} = \begin{bmatrix} v(t) \\ a(t) \\ j(t) \end{bmatrix}
In discrete form (for real-time computation):
x_{k+1} = x_k + v_k \Delta t + \frac{1}{2} a_k \Delta t^2 + \frac{1}{6} j_k \Delta t^3
This equation is crucial in prediction for real-time interception.
---
🧠 Why Third-Order Calculus Matters for Iron Dome
Use Case Why Jerk Matters
Trajectory prediction Missiles may accelerate unpredictably — jerk-aware models predict better
Kalman filtering Adds precision to dynamic state estimation
Missile control Smooth guidance without instability in fast turns
Avoid false positives Helps differentiate between real threats and decoys
Compute intercept course Higher-order motion modeling ensures better accuracy in impact prediction
---
🔐 Final Thoughts
While the exact implementation of the Iron Dome is classified, it's virtually certain that third-order calculus is part of its:
Target prediction algorithms
Real-time control systems
Sensor fusion and filtering
Guidance system
---
Great follow-up. Let’s explore third-order calculus in the context of the David's Sling missile defense system — a more advanced and longer-range complement to the Iron Dome, designed to intercept medium- to long-range ballistic and cruise missiles.
---
🛡️ What Is David’s Sling?
David's Sling is a missile defense system designed by Israel (with U.S. collaboration) to intercept threats at longer ranges, such as:
Ballistic missiles
Cruise missiles
Drones and aircraft
Its core interceptor missile is the Stunner, which uses advanced multi-sensor guidance and electro-optical tracking to engage threats at high altitudes and long distances.
---
📘 Where Third-Order Calculus Is Used
In such systems, third-order calculus refers to modeling and using:
Position (0th derivative)
Velocity (1st derivative)
Acceleration (2nd derivative)
Jerk (3rd derivative: )
Tracking high-speed, maneuverable threats — such as cruise missiles — requires modeling motion up to jerk for effective prediction, guidance, and interception.
---
🧠 1. State Estimation with Third-Order Dynamics
State vector:
\mathbf{x} = \begin{bmatrix}
x \\
v \\
a
\end{bmatrix}
Where:
: position vector (3D)
: velocity
: acceleration
: jerk (modeled as either deterministic or process noise)
In real-time Kalman filters, you may assume:
\dot{x} = v,\quad \dot{v} = a,\quad \dot{a} = j
This makes it a third-order dynamic system, with jerk either known, estimated, or assumed to be stochastic noise (e.g., Gaussian white noise with known covariance).
---
📡 2. Missile Guidance with Third-Order Control
The Stunner interceptor uses high-speed maneuvering and needs accurate modeling of its own and the target's dynamics. Including jerk helps:
Predict evasive targets
Avoid control lag from delayed acceleration response
Reduce intercept error from abrupt maneuvering
Missile control system can include:
\frac{d^3x}{dt^3} = j(t) = \text{Control input}
So you design a controller that tracks not just desired position or velocity, but also smoothness (minimizing jerk).
---
🛰️ 3. Trajectory Prediction in Tracking Radar
The radar system (ground-based or onboard) tracking an incoming missile uses:
Continuous target position updates
Filters that incorporate jerk to reduce overshoot in predicted trajectory
If the target performs nonlinear maneuvers (common in advanced ballistic missiles), using only acceleration isn’t enough. Third-order prediction significantly increases accuracy.
---
📐 Mathematical Model (Continuous-Time)
The third-order model:
\begin{bmatrix}
\dot{x} \\
\dot{v} \\
\dot{a}
\end{bmatrix}
=
\begin{bmatrix}
v \\
a \\
j
\end{bmatrix}
This leads to a third-order differential equation for position:
\frac{d^3x}{dt^3} = j(t)
In guidance laws (e.g., model predictive control), this might be part of a control objective:
Minimize jerk
Meet time-to-target
Avoid overshoot
---
🧮 Discrete-Time Model (for Implementation)
In real-time systems (DSP or embedded), we discretize:
x_{k+1} = x_k + v_k \Delta t + \frac{1}{2} a_k \Delta t^2 + \frac{1}{6} j_k \Delta t^3
Used in trajectory estimation and prediction
Implemented using digital filters (like an extended Kalman filter)
---
✅ Summary: 3rd-Order Calculus in David’s Sling
System Component Use of 3rd-Order Calculus
Stunner missile Uses jerk-based control for precision guidance
Radar tracking Third-order filters improve path prediction
Fire control system Estimates target's future position by modeling jerk
Kalman filters Track position, velocity, acceleration; model jerk as noise
Trajectory prediction Handles evasive threats or curved cruise missile paths
7th-order differential and integral equations are advanced mathematical constructs often used in fields like physics, control systems, and engineering where complex dynamic systems are modeled. Here's a breakdown of what they are:
---
🔹 7th-Order Differential Equation
A 7th-order differential equation involves derivatives up to the seventh derivative of a function.
📘 General Form:
\frac{d^7y}{dt^7} + a_6\frac{d^6y}{dt^6} + a_5\frac{d^5y}{dt^5} + \dots + a_1\frac{dy}{dt} + a_0y = f(t)
: constant coefficients
: an input or forcing function (can be zero for homogeneous case)
✅ Example:
\frac{d^7y}{dt^7} - 3\frac{d^6y}{dt^6} + 5y = \sin(t)
Used in:
Control Systems with high dynamics (e.g., aerospace, missile systems)
Mechanical vibrations with multiple degrees of freedom
Wave propagation in layered media
---
🔹 7th-Order Integral
A 7th-order integral is the repeated integration of a function seven times.
📘 General Idea:
I^7[f(t)] = \int \left( \int \left( \dots \int f(t) \, dt \dots \right) \right) dt
I^n[f(t)] = \underbrace{\int \dots \int}_{n \text{ times}} f(t) \, dt^n
✅ Example:
Let , then the 7th-order integral is:
I^7[t] = \frac{t^8}{8!} + C_1t^6 + C_2t^5 + \dots + C_7
---
🧠 Combined in Systems
In system modeling, especially with state-space models or transfer functions, high-order derivatives and integrals help describe the behavior of dynamic systems. For instance:
Missile guidance systems (like David’s Sling or Iron Dome) may require 7th-order models to represent physical dynamics, noise, filtering, and estimation precisely.
---
Here's an example of a 7th-order differential system applied in an electronic control system, along with a conceptual block diagram using state-space modeling.
---
🔧 Example: 7th-Order Electronic Control System
Let’s model a high-performance missile guidance system (like David's Sling or Iron Dome) using a 7th-order differential equation. This can represent:
3rd order for mechanical position
2nd order for sensor dynamics
2nd order for filtering or estimator correction
🧮 Differential Equation Form:
\frac{d^7y}{dt^7} + a_6\frac{d^6y}{dt^6} + a_5\frac{d^5y}{dt^5} + \cdots + a_0y = b_0u(t)
Where:
: output (e.g., missile angular position or altitude)
: input (control signal from guidance unit)
: constants based on physical modeling and tuning
---
📊 State-Space Representation (7th Order)
Let’s define state variables:
x_1 = y, \quad x_2 = \dot{y}, \quad x_3 = \ddot{y}, \quad \dots, \quad x_7 = y^{(6)}
🌐 State Equations:
\dot{x}_1 = x_2 \\
\dot{x}_2 = x_3 \\
\dot{x}_3 = x_4 \\
\dot{x}_4 = x_5 \\
\dot{x}_5 = x_6 \\
\dot{x}_6 = x_7 \\
\dot{x}_7 = -a_6x_7 - a_5x_6 - \dots - a_0x_1 + b_0u(t)
🧩 Block Diagram Components:
Here’s the layout:
+--------+ +--------+ +--------+ +--------+
-->| x7dot |<----| x6 |<----| x5 |<----| x4 |<--
+--------+ +--------+ +--------+ +--------+
^ |
| v
+--------+ +--------+ +--------+ +--------+
-->| x3 |<----| x2 |<----| x1 |<----| Input |
+--------+ +--------+ +--------+ +--------+
|
Output (y)
This block diagram reflects 7 integrators in series, each representing one state , going from the highest derivative (7th) to the actual output.
---
🔍 Applications in Real Systems
This model could represent:
Missile pitch control system
Adaptive radar filtering
State estimator in defense systems (e.g., Kalman filter of 7th order)
---
Design system electronic control networking system 7th orde calculus and differential
and integral to geometry analytic :
"Mathematic Bunker Buster Boom" — sounds like a code name or a poetic metaphor for an intense, precision-targeted mathematical idea or technique. Let's break this down creatively and technically:
---
🔥 Conceptual Interpretation:
"Mathematic": Logic, precision, structure.
"Bunker Buster": A weapon designed to penetrate deep fortifications.
"Boom": The explosive impact — metaphorically, a breakthrough or powerful result.
Put together, it could symbolize:
> “A high-impact mathematical method or discovery designed to break through the deepest problems or toughest equations.”
---
💣 Mathematical Applications That Could Be “Bunker Busters”:
Here are some real examples in advanced mathematics and applied science that act like “bunker busters” — powerful tools that solve deep problems:
1. Fourier Transform – Penetrates complex waveforms and uncovers hidden frequencies.
2. Laplace Transform – A powerful tool in control systems and differential equations — reduces dynamics into algebraic simplicity.
3. Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) – Models for heat, wave, and quantum mechanics — hard problems needing strong math "ammo."
4. Numerical Simulations + Finite Element Analysis (FEA) – Crushes real-world engineering challenges with approximate solutions.
5. Cryptographic Number Theory – Breaks or protects digital fortresses using prime numbers and modular arithmetic.
6. Control Theory (e.g., 3rd/7th-order systems) – Used in missile guidance, radar, and defense systems — including real bunker busters like the GBU-57A/B.
---
🧠 Hypothetical “Math Bunker Buster Boom” Scenario:
Imagine this:
> You're designing a missile trajectory to breach an underground nuclear facility. You need to:
Estimate the depth and location using GPS signals (filtered with Kalman filters, a 3rd-order or higher state estimator).
Solve 7th-order differential equations for motion + resistance + gravity + blast timing.
Use nonlinear optimization to fine-tune detonation based on material density.
A "manoeuvre circuit concept" in electronics or control systems generally refers to a circuit that performs dynamic actions or adaptive responses, often for navigation, robotics, automation, or missile defense systems.
Here’s a complete concept overview and a basic schematic idea:
---
🧠 Maneuver Circuit Concept: Overview
🔧 Definition:
A maneuver circuit is an electronic control loop or signal processing system that allows a machine or device (e.g., drone, robot, guided missile) to change direction, adjust position, or respond to environment changes.
---
🧩 Key Functional Blocks
1. Sensors & Inputs
Gyroscope / Accelerometer – Detects movement and orientation.
GPS Module – For position tracking.
IR / Radar / Camera – Detects obstacles or targets.
2. Processing Unit
Microcontroller (e.g., STM32, Arduino, etc.)
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) for fast calculations.
Executes path correction algorithms (e.g., PID control, Kalman filter).
3. Control Logic Circuit
Maneuver decision logic (e.g., turn left/right, ascend/descend).
Multiplexers / Logic Gates if done in discrete digital form.
PWM Generators for motor control.
4. Actuator Drivers
Motor driver ICs (e.g., L298N) – Control movement.
Servo/Stepper Controllers – Precision control.
5. Feedback Loop
Real-time correction (closed-loop system)
Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control adjusts trajectory.
---
🔌 Schematic Concept: Simplified
[Sensor Block]
(Gyro, GPS, Radar)
↓
[Microcontroller / DSP]
↓
[Control Logic Circuit]
(PWM Gen + Logic + PID)
↓
[Motor / Servo Driver]
↓
[Actuators (Motors, Fins)]
↓
[Feedback Sensors] ←─────
---
🎯 Application Areas
Application Function of Maneuver Circuit
Missiles / UAVs Target homing & evasion
Autonomous Cars Lane keeping & turning
Robotics Directional control
Aerospace Navigation Orbital adjustments
Game Simulators Real-time directional inputs
---
Cryptography Technical for Military and Aerospace as like as B2 stealth Bomber
==============================================================================
A cryptography system is a framework used to secure communication and protect information by converting it into a form that unauthorized parties cannot understand. It relies on mathematical algorithms and keys to encrypt (hide) and decrypt (reveal) data.
---
🔐 Basic Components of a Cryptography System
1. Plaintext: The original, readable message or data.
2. Ciphertext: The scrambled, unreadable version after encryption.
3. Encryption Algorithm: A formula that transforms plaintext into ciphertext.
4. Decryption Algorithm: Reverses encryption to get plaintext back.
5. Key: A string of bits used in the algorithms. Can be:
Symmetric (same key for encryption and decryption)
Asymmetric (public key for encryption, private key for decryption)
---
🔑 Types of Cryptography
Type Description Example Algorithms
Symmetric-key cryptography Same key used for both encryption and decryption AES, DES, RC4
Asymmetric-key cryptography Uses a public and private key pair RSA, ECC
Hash Functions Converts data to fixed-length hash, no decryption SHA-256, MD5
---
🧠 Key Concepts
Confidentiality: Only authorized parties can read the data.
Integrity: Data hasn’t been altered (e.g. via hash functions).
Authentication: Verifying the identity of sender/receiver.
Non-repudiation: Sender cannot deny sending a message (e.g. digital signatures).
---
🛰️ Cryptography in Use
Messaging Apps (WhatsApp, Signal)
Secure Websites (HTTPS/SSL)
Banking & ATM Systems
Military Communication Systems (e.g., Iron Dome, B2 Stealth encrypt radar signals)
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency (Bitcoin, Ethereum)
Cryptography is crucial in satellites and military systems to ensure secure, reliable, and tamper-resistant communication and data handling. Here's how it's used:
---
🛰️ In Satellite Systems
1. Secure Uplink/Downlink Communication
Data from ground stations to satellites (uplink) and back (downlink) is encrypted to prevent interception or spoofing.
Example: GPS signals use military-grade encryption (M-code) to avoid spoofing and jamming.
2. Command Authentication
Commands sent to satellites (e.g., orbital adjustments, shutdowns) are signed and verified with cryptographic keys to ensure they’re from authorized sources.
3. Telemetry Protection
Telemetry (health and status data) from satellites is encrypted to prevent adversaries from learning satellite vulnerabilities.
---
🛡️ In Military Systems
1. End-to-End Encrypted Communication
All radio, satellite, and network communications between soldiers, units, aircraft, drones, and command centers use cryptography (e.g., AES-256, ECC, custom military ciphers).
2. Weapon System Security
Advanced weapons like the Iron Dome, David’s Sling, B2 Stealth Bomber rely on encrypted radar, telemetry, and target data to avoid hacking or jamming.
3. Authentication & Access Control
Only authorized personnel with the right keys or cryptographic tokens can access systems (e.g., nuclear launch protocols use multi-level crypto authentication).
4. Cyber Defense
Military systems employ cryptographic firewalls, VPNs, and secure boot processes to protect against cyberattacks.
5. Stealth and Counter-Stealth
Encryption is used in low-probability-of-intercept (LPI) systems to hide radar and comms from enemy detection.
---
🔑 Technologies Used
AES, RSA, ECC, SHA-2/3 for encryption/hashing
Quantum key distribution (QKD) in next-gen secure satellites
HMAC, Digital Signatures for message integrity and source validation
Blockchain (experimental) in satellite telemetry for tamper-proof logs .
Here are key electronic components used for encryption and decryption in both analog and digital systems:
---
🔐 1. Digital Components
These are used in modern, real-world encryption systems.
Component Function Example
Microcontroller (MCU) Processes encryption/decryption algorithms Arduino, STM32, ATmega328
Microprocessor High-speed data encryption (e.g., AES, RSA) ARM Cortex, Intel, ESP32
XOR Gate (IC 7486) Logic-based bitwise encryption (XOR logic) Basic hardware encryption
EEPROM / Flash Memory Stores encrypted data or keys 24C32, 25LC640
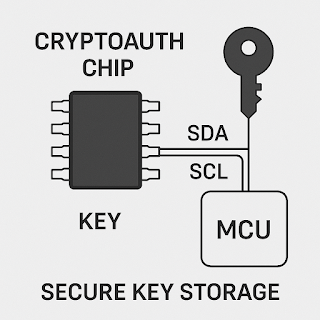
Crypto IC (Dedicated) Hardware encryption module Microchip ATECC608A, Infineon OPTIGA Trust
FPGA Implements high-speed custom crypto logic Xilinx Spartan, Intel Cyclone
---
📻 2. Analog/Discrete Components
Used in low-level circuits or supporting systems.
Component Function Example
Transistor (NPN/PNP) Switch or amplify signals in logic levels 2N3904, BC547
Resistor Voltage divider for digital logic levels 1kΩ, 10kΩ
Capacitor Filter noise in signal or power lines 100nF, 10µF
Diode Protect or shape digital signals 1N4148
Optocoupler Isolate secure logic signal PC817
---
🛰️ 3. Modules & Chips for Secure Communication
Used in military, satellite, or secure IoT devices.
Chip/Module Function
TPM (Trusted Platform Module) Cryptographic key storage and secure boot
ATECC608A Secure key storage, ECC encryption
LoRa Module (with AES) Secure long-range communication
Secure SIM Card (UICC) Encrypted cellular authentication
GPS Modules (military-grade) Encrypted M-code for anti-spoofing
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)